Pidolic Acid: The Power, Functions, Benefits & Applications
Pidolic acid, also known as 5-oxoproline or L-pyroglutamic acid, is a naturally occurring amino acid derivative found in various tissues throughout the human body. While its role in metabolism has been studied for decades, recent research has shed new light on its significance in maintaining overall health. In this blog post, we’ll delve into the fascinating world of pidolic acid, exploring its functions, potential benefits, and ongoing research.
What is Pidolic Acid?
Pidolic acid is a cyclic form of glutamic acid, a common amino acid involved in protein synthesis and energy production. It is primarily found in the brain, skin, and other tissues, where it plays a crucial role in various metabolic pathways [1]. Pidolic acid, a lesser-known amino acid derivative, plays a crucial role in various biological processes. Pidolic acid is a naturally occurring compound found in the human body, formed when the amino group of glutamic acid or glutamine creates a ring-shaped structure called a lactam [2].
This naturally occurring compound can be synthesized both enzymatically and non-enzymatically, and its unique pharmacological properties make it a promising target for research in the field of (relevant field, e.g., drug discovery, biochemistry).

Pidolic Acid: A Natural Chelator
Pidolic acid acts as a natural chelator, forming stable complexes with metal ions such as zinc, copper, and iron. This chelation process involves the formation of coordinate bonds between the electron-rich oxygen atoms of pidolic acid and the positively charged metal ions [3]. By binding to these metal ions, pidolic acid prevents their interactions with other molecules, which can be detrimental to cellular function. This chelating property is particularly important for preventing the accumulation of excess metal ions, which can lead to toxicity. Additionally, chelation by pidolic acid can enhance the bioavailability of essential minerals by promoting their absorption from the digestive tract and transport to target tissues [4].
Pidolic Acid Structure
Pidolic acid, also known as 5-oxoproline or L-pyroglutamic acid, is a cyclic derivative of glutamic acid. Pidolic acid is a valuable chemical compound synthesized through a multi-step process involving oxidation of d-isoquercitrin [5]. Pidolic acid, a phenolic acid derived from quercetin, has a unique molecular structure featuring a benzene ring with multiple hydroxyl groups. Its structure features a five-membered ring containing a carbonyl group (C=O) and an amide group (NH) [6]. This cyclic configuration renders pidolic acid more stable and resistant to hydrolysis compared to its linear counterpart, glutamic acid [7].
The unique structural features of pidolic acid contribute to its distinct properties and biological functions, including its ability to form complexes with minerals and its role in various metabolic pathways.
Pidolic Acid Functions
Pidolic acid possesses antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, making it a promising compound for various applications in the pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries.
- Glutathione Metabolism: Pidolic acid is a key intermediate in the glutathione cycle, a vital pathway for detoxification and antioxidant defence [8]. It is involved in the recycling of glutathione, a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Neurotransmitter Regulation: Studies have suggested that pidolic acid may influence the levels of certain neurotransmitters, such as acetylcholine, which plays a role in memory, learning, and muscle function [9].
- Skin Health: Pidolic acid is found in high concentrations in the skin, where it may contribute to its structural integrity and hydration. Some research has indicated that it could have potential applications in skincare products for improving skin elasticity and reducing wrinkles.
- Metabolism: Pidolic acid uses may influence metabolic processes, potentially impacting factors such as weight management and energy expenditure [10].
- Antioxidant Properties: Pidolic acid itself possesses antioxidant properties, which may help protect cells from oxidative stress and contribute to overall health.
- Anti-inflammatory Properties: Pidolic acid possesses potent anti-inflammatory properties, making it a promising candidate for the treatment of inflammatory diseases such as arthritis and autoimmune disorders [11].
Potential Pidolic Acid Benefits
Pidolic acid’s versatility lies in its ability to form complexes with various minerals, enhancing their bioavailability and biological activity. These complexes can act as chelators, binding to metal ions and preventing their interactions with other molecules. This property is particularly important for trace minerals like zinc, copper, and iron, which are essential for numerous physiological functions [12].
By forming complexes with these minerals, pidolic acid can improve their absorption from the digestive tract, transport to target tissues, and utilization by cells. This synergistic relationship between pidolic acid and minerals highlights its crucial role in maintaining optimal health and preventing mineral deficiencies [13]. Based on its functions and preliminary research, pidolic acid may offer several potential benefits, including:
- Improved cognitive function: Its involvement in neurotransmitter regulation suggests it could support memory and learning.
- Enhanced skin health: Pidolic acid’s presence in the skin could contribute to a youthful and healthy complexion [14].
- Enhanced detoxification: As part of the glutathione cycle, it may aid in removing harmful toxins from the body.
- Reduced oxidative stress: Its antioxidant properties could help protect cells from damage caused by free radicals.
- Pidolic acid in plants: L-PGA (Pidolic Acid) is a valuable nutrient that enhances plant growth by optimizing nitrogen uptake and assimilation [15,16]. This natural compound also stimulates photosynthesis, allowing plants to capture more carbon and effectively utilize nitrogen for robust development.
- Pidolic acid in cancer: Pidolic acid has demonstrated potential anti-cancer properties in laboratory studies, suggesting its potential as a therapeutic agent for certain types of cancer.
- Therapeutic applications: Pidolic acid is a promising compound with potential therapeutic applications, but there are currently no commercially available medicines that specifically utilize it as an active ingredient for any medical condition.
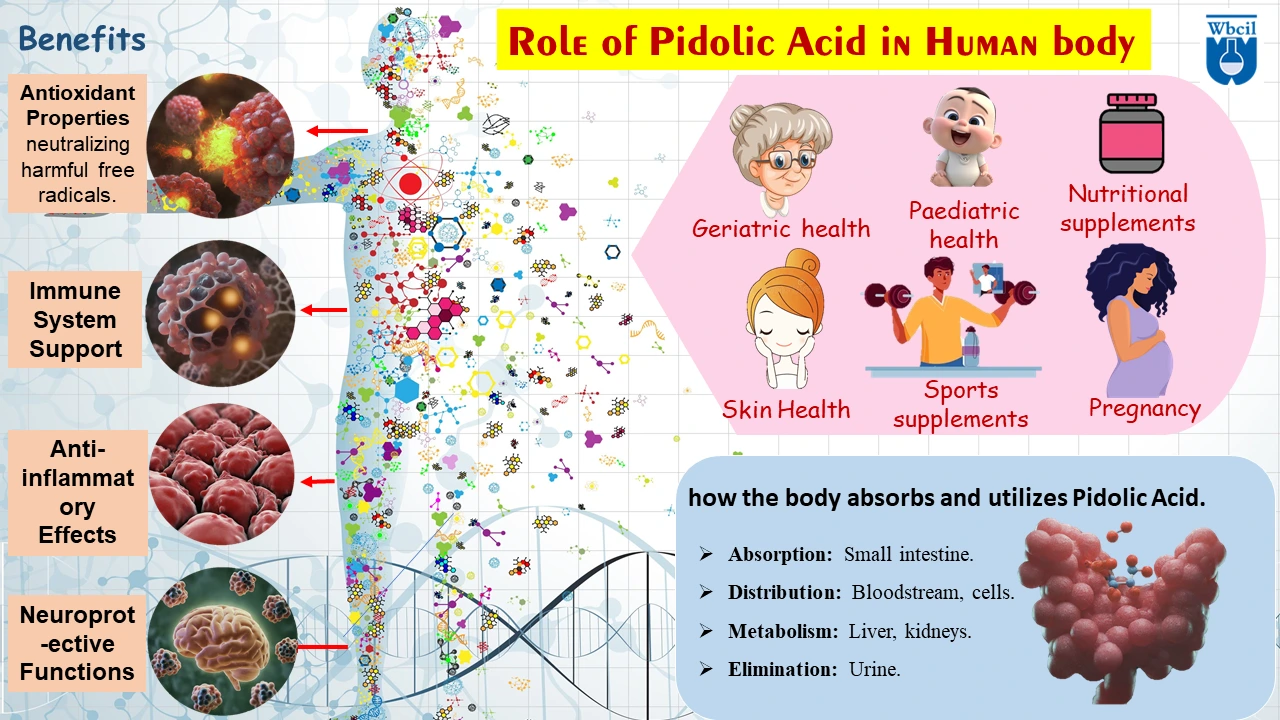
Ongoing Research
Pidolic acid has potential applications in the development of new drugs for various diseases, including cancer and inflammation, due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties. While the research on pidolic acid is still ongoing, there is increasing interest in its potential applications in various fields, including:
- Pidolic acid and geriatric care: Studies are exploring its role in conditions such as Alzheimer’s disease and Parkinson’s disease [17]. Pidolic acid has shown potential benefits for neurological disorders in preclinical studies, suggesting its possible role in mitigating the progression of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s.
- Pidolic acid for pediatric health: Pidolic acid, with its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, has potential applications in pediatric health, particularly in the prevention and treatment of childhood diseases [18].
- Skincare: Pidolic acid is being investigated for its potential use in topical skincare products.
- Nutritional supplements: There is growing interest in developing supplements containing pidolic acid to support overall health.
- Pidolic acid in sports supplement: Pidolic acid, due to its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, is being explored as a potential ingredient in sports supplements to support athletic performance and recovery [19].
- Pidolic acid benefits for pregnancy: While research on pidolic acid supplements during pregnancy is limited, its antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties suggest potential benefits for maternal and fetal health, though more studies are needed.
Pidolic Acid Suppliers
Pidolic acid is available from a variety of chemical suppliers, both online and offline, offering high-quality products for research, development, and industrial applications. As a manufacturer of Pidolic Acid APIs, we offer a variety of product options to cater to diverse customer needs [20,21]. These APIs can vary in purity levels, particle size, and specific applications. For instance, we provide high-purity Pidolic Acid APIs suitable for research and development purposes, as well as pharmaceutical-grade APIs that meet stringent quality standards for use in drug formulations.
We offer Calcium pidolate and magnesium pidolate [22]. Our goal is to provide our customers with reliable and high-quality Pidolic Acid APIs that meet their unique needs and contribute to advancements in various fields, including pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and cosmetics.
Conclusion
Pidolic acid is a fascinating molecule with a vital role in human metabolism. As research continues to uncover its diverse functions and potential benefits, it is likely that we will see increased interest in this underappreciated compound. Whether it’s for improving cognitive function, enhancing skin health, or supporting overall well-being, pidolic acid may offer promising possibilities for the future.
1. Wikipedia contributors. Pyroglutamic acid. Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia. April 12, 2024, 12:06 UTC. Available at: https://en.wikipedia.org/w/index.php?title=Pyroglutamic_acid&oldid=1218554774. Accessed September 10, 2024.
2. National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 7405, L-Pyroglutamic acid. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/L-Pyroglutamic-acid
3. https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/medicine-and-dentistry/pyroglutamic-acid
4. https://echa.europa.eu/lt/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.002.455
5. https://webbook.nist.gov/cgi/cbook.cgi?ID=98-79-3
6. https://www.guidetopharmacology.org/GRAC/LigandDisplayForward?ligandId=4703
7. Jiménez-Arias, David; García-Machado, Francisco J.; Morales-Sierra, Sarai; Luis, Juan C.; Suarez, Emma; Hernández, Mercedes; Valdés, Francisco; Borges, Andrés A. . (2018). Lettuce plants treated with L-pyroglutamic acid increase yield under water deficit stress. Environmental and Experimental Botany, (), S0098847218312279–. https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0098847218312279
8. National Center for Biotechnology Information. PubChem Compound Summary for CID 499, DL-Pyroglutamic acid. https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/DL-Pyroglutamic-acid
9. https://litfl.com/pyroglutamic-acidosis/
10. https://www.rcsb.org/ligand/PCA
11. Gueta, I., Perach Ovadia, Y., Markovits, N. et al. Is Pyroglutamic Acid a Prognostic Factor Among Patients with Suspected Infection? A Prospective Cohort Study. Sci Rep 10, 10128 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-66941-7
12. Chandramouli Lalam, Naidu Petla, Srinivasan Tantravahi. (2021). Antiproliferative and Antibacterial Effects of Pyroglutamic Acid Isolated from Enterococcus Faecium (Mcc-2729). Annals of the Romanian Society for Cell Biology, 7624–7628. Retrieved from http://annalsofrscb.ro/index.php/journal/article/view/2305
13. https://www.chemicalbook.in/product/l-pyroglutamic-acid-9197008
14. Kumar, A., & Bachhawat, A. K. (2012). Pyroglutamic acid: throwing light on a lightly studied metabolite. Current Science, 102(2), 288–297. http://www.jstor.org/stable/24083854
15. Dirk Chelius, Kay Jing, Alexis Lueras, Douglas S. Rehder, Thomas M. Dillon, Alona Vizel, Rahul S. Rajan, Tiansheng Li, Michael J. Treuheit, and Pavel V. Bondarenko
16. Analytical Chemistry 2006 78 (7), 2370-2376
17. DOI: 10.1021/ac051827k. https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/ac051827k
18. CSID:7127, https://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.7127.html, (accessed 11:35, Sep 10, 2024). https://www.chemspider.com/Chemical-Structure.7127.html
19. Preparation method of pyroglutamic acid, CN103351323A, China. https://patents.google.com/patent/CN103351323A/en
20. Emmett, Michael. Acetaminophen Toxicity and 5-Oxoproline (Pyroglutamic Acid): A Tale of Two Cycles, One an ATP-Depleting Futile Cycle and the Other a Useful Cycle. Clinical Journal of the American Society of Nephrology 9(1):p 191-200, January 2014. | DOI: 10.2215/CJN.07730713. https://journals.lww.com/cjasn/fulltext/2014/01000/acetaminophen_toxicity_and_5_oxoproline.26.aspx
21. https://efsa.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/pdf/10.2903/j.efsa.2007.495
22. Kumar, A., & Bachhawat, A.K. (2012). Pyroglutamic acid : throwing light on a lightly studied metabolite. https://www.semanticscholar.org/paper/Pyroglutamic-acid-%3A-throwing-light-on-a-lightly-Kumar-Bachhawat/c50e3ad15345b8901709d52d89f38c1c0fb6080c
Pidolic acid, also known as 5-oxoproline or L-pyroglutamic acid, is a naturally occurring derivative of the amino acid glutamic acid. It plays a significant role in various metabolic processes in the body, particularly in the brain, skin, and other tissues.
Pidolic acid has multiple potential benefits, including:
Enhancing cognitive function by regulating neurotransmitters.
Supporting skin health through its presence in skin tissues.
Acting as a natural chelator, enhancing the bioavailability of essential minerals like zinc and copper.
Reducing oxidative stress due to its antioxidant properties.
Supporting metabolism and detoxification through the glutathione cycle.
Pidolic acid binds to metal ions such as zinc, copper, and iron, forming stable complexes. This chelation process prevents excess metal ions from accumulating in the body, protecting cells from potential toxicity and enhancing the absorption and transport of essential minerals.
Pidolic acid is a key intermediate in the glutathione cycle, a critical pathway for detoxification and antioxidant defense in the body. It helps recycle glutathione, a powerful antioxidant that protects cells from free radical damage.
Yes, Pidolic acid is found in high concentrations in the skin and may contribute to skin elasticity, hydration, and overall structural integrity. Some research suggests its potential use in skincare products to reduce wrinkles and improve skin health
Yes, Pidolic acid possesses potent anti-inflammatory properties, which make it a promising candidate for treating inflammatory diseases like arthritis and autoimmune disorders.
In plants, L-Pidolic Acid plays a vital role in enhancing nitrogen uptake and stimulating photosynthesis. This leads to better nitrogen assimilation and robust plant growth.
Yes, ongoing research is exploring the potential of Pidolic Acid in treating neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s. It also shows promise in cancer treatment and pediatric health applications.
Currently, there is growing interest in developing supplements that include Pidolic Acid due to its antioxidant and chelating properties. West Bengal Chemical Industries Limited is now manufacturing calcium and magnesium pidolate. However, more research is needed to fully establish its use in supplement form.


