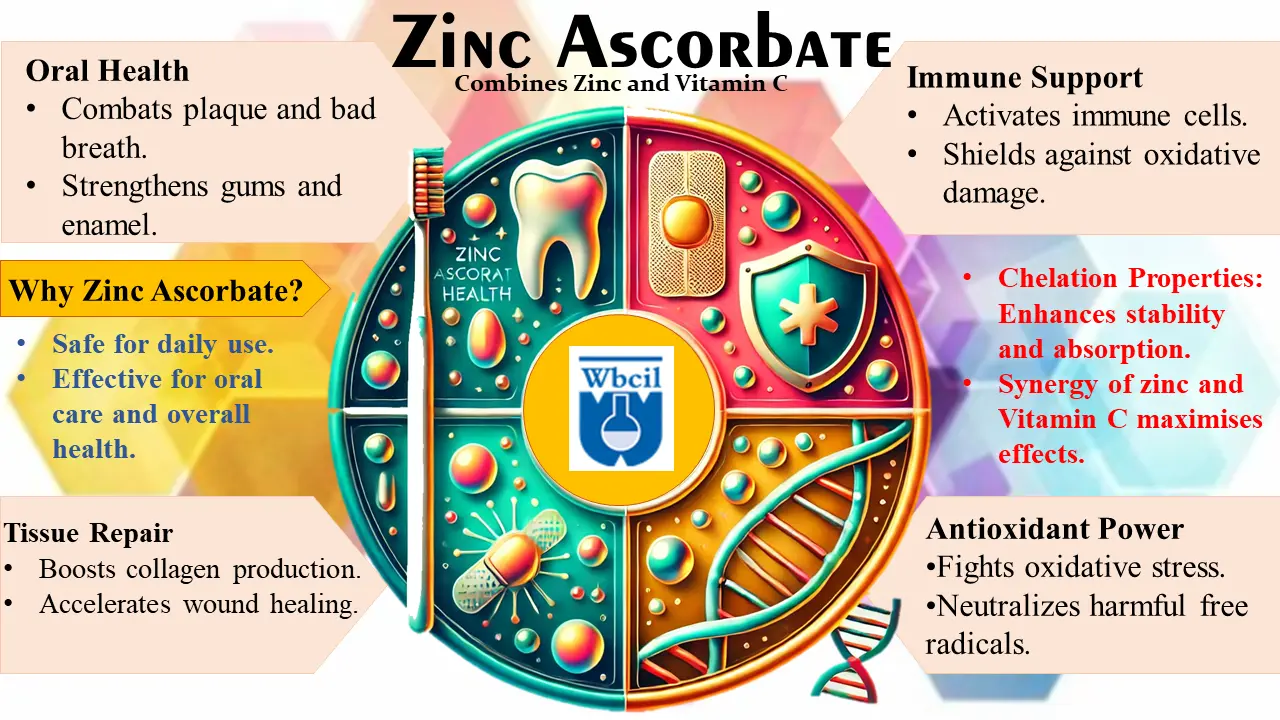
Zinc Ascorbate: The Dynamic Duo Revolutionizing Oral Health and Beyond
When it comes to health, combining the right elements can create something extraordinary. One such combination is zinc ascorbate—a powerhouse compound derived from zinc and ascorbic acid (Vitamin C). Together, these two nutrients amplify each other’s effects, offering benefits far beyond their standalone capabilities. But what exactly makes zinc ascorbate so special? Let’s dive into the science and discover why this duo deserves a spot in your health and wellness routine.
What is Zinc Ascorbate?
Zinc ascorbate is a compound formed by combining zinc, an essential mineral, with ascorbic acid, a critical antioxidant. These two components play vital roles in numerous biological processes, including immune function, tissue repair, and oral health. While each has individual benefits, their combination in zinc ascorbate creates a synergy that maximizes their potential.
- Zinc: Known for its role in enzymatic functions, immunity, and wound healing [1].
- Ascorbic Acid (Vitamin C): Famous for its antioxidant properties, collagen production, and immune support [2].
Together, they form a bioavailable compound that’s readily absorbed in the body and acts as a multitasking health booster.

Zinc Ascorbate: A Chelated Compound
One of the key scientific properties that make zinc ascorbate effective is its chelation-like nature.
What is Chelation?
Chelation occurs when a metal ion (like zinc) binds to an organic molecule (a ligand) through multiple coordinate bonds, forming a stable complex [3]. Chelated minerals are often more bioavailable, better absorbed, and more effective than their inorganic counterparts.
Zinc Ascorbate as a Chelate
In zinc ascorbate, ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) acts as the ligand, binding to zinc ions and forming a coordination complex. This process offers several benefits:
- Enhanced Stability: The zinc-ascorbate complex is stable, preventing premature dissociation and ensuring the compound remains intact until it reaches the target site in the body.
- Improved Absorption: Chelated forms of zinc, including zinc ascorbate, are more bioavailable [4]. The organic ligand (ascorbic acid) helps transport zinc efficiently through the digestive tract.
- Synergistic Health Effects: Ascorbic acid not only enhances zinc’s stability but also amplifies its benefits, especially for immune function, antioxidant activity, and tissue repair.
Zinc ascorbate shares many chelation-like properties. This combination ensures that both zinc and ascorbic acid work together efficiently, boosting their overall impact on health.
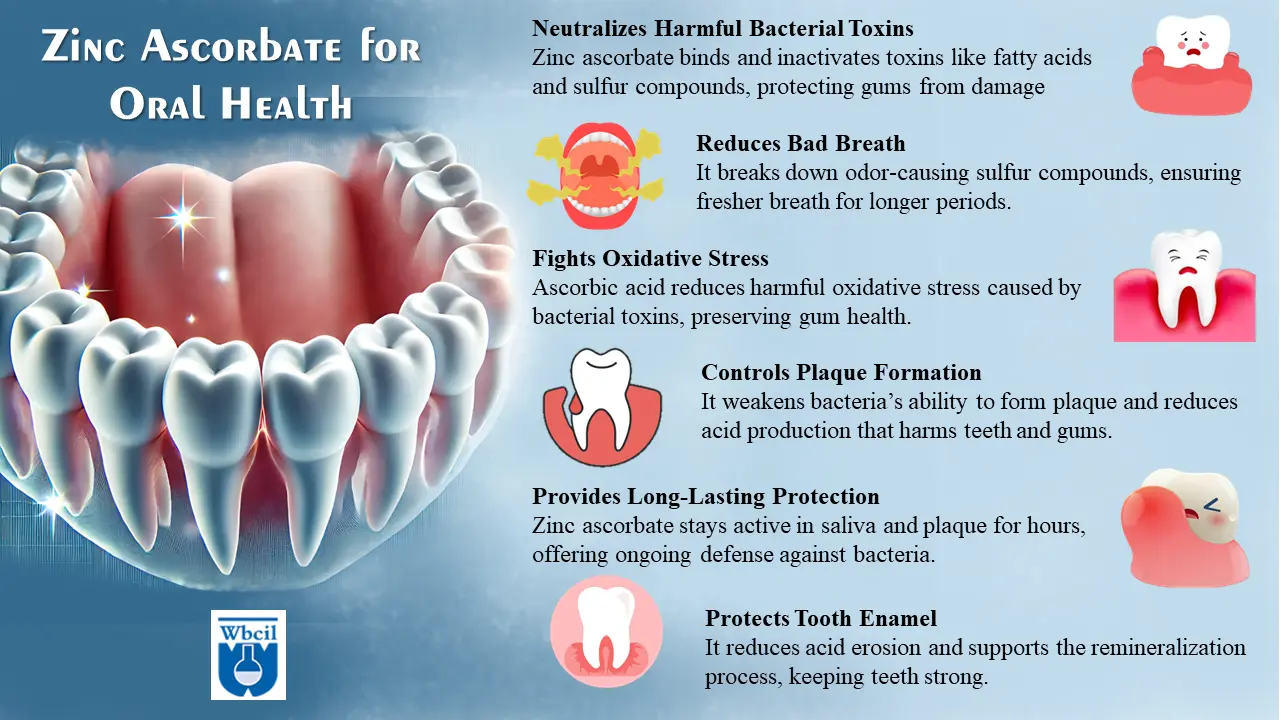
Oral Health: A Winning Smile Starts Here
The first place where zinc ascorbate shines is in oral care. Think of your oral cavity as a bustling ecosystem—home to bacteria, enzymes, and soft tissues, all working in delicate balance [5]. Zinc ascorbate steps in to ensure harmony, offering benefits such as:
- Antibacterial Action: Zinc inhibits harmful bacteria like Porphyromonas gingivalis, a key player in gum disease. It also prevents plaque buildup by oxidizing bacterial films.
- Stronger Gums: Ascorbic acid promotes collagen synthesis, repairing and strengthening gum tissues, while zinc ensures this collagen is stabilized and durable [6].
- Enamel Protection: Zinc replaces calcium in enamel hydroxyapatite, reinforcing tooth structure and preventing demineralization.
- Fresh Breath: Zinc binds volatile sulfur compounds that cause halitosis, keeping your breath fresh and pleasant.
Imagine brushing your teeth and knowing that zinc ascorbate is not only cleaning but also healing and protecting your mouth for hours afterward!
Immune Support: Building a Shield Against Invaders
Zinc and ascorbic acid are both renowned for bolstering the immune system, but together in zinc ascorbate, their effects are supercharged:
- Zinc’s Role: Activates immune cells like neutrophils, macrophages, and T-lymphocytes, helping your body identify and destroy harmful invaders.
- Ascorbic Acid’s Contribution: Enhances antibody production and protects immune cells from oxidative damage, prolonging their efficiency during infections [7].
- The Synergy: Zinc creates the soldiers (immune cells), while ascorbic acid equips them with shields (antioxidant protection), forming a two-layered defense system.
Whether it’s a cold, a wound, or an oral infection, zinc ascorbate supports your immune system in fighting off pathogens effectively and efficiently.
Tissue Repair: The Ultimate Healer
Injuries—whether in the oral cavity or elsewhere—require swift and effective healing. Zinc ascorbate excels here as well:
- Collagen Production: Ascorbic acid drives the creation of collagen, the structural protein that holds tissues together.
- Collagen Stability: Zinc ensures that the collagen produced is cross-linked and stable, making it stronger and more resilient [8].
- Wound Healing: Zinc promotes keratinocyte migration and re-epithelialization, speeding up skin and tissue repair.
This duo doesn’t just heal wounds; it ensures the repaired tissues are stronger and more resistant to future damage.
- Boosting Ascorbic Acid Benefits with Zinc
While ascorbic acid is already a powerful nutrient, zinc significantly enhances some of its core benefits, creating a unique synergy in zinc ascorbate. Here’s how:
- Enhanced Collagen Stability: Ascorbic acid initiates collagen synthesis, but zinc stabilizes the collagen matrix, making it more durable and resistant to degradation. This is crucial for oral health, skin healing, and vascular integrity.
- Prolonged Antioxidant Action: Ascorbic acid neutralizes free radicals, but its effectiveness is extended in the presence of zinc, which reduces the production of new reactive oxygen species (ROS) [9].
- Strengthened Immune Responses: While ascorbic acid boosts the activity of immune cells, zinc enhances their development and ensures they remain functional for longer periods, improving the overall immune response.
- Faster Healing: Ascorbic acid drives tissue regeneration, while zinc accelerates re-epithelialization and ensures the structural integrity of new tissues, speeding up recovery [10].
- Increased Bioavailability: Zinc’s role as a stabilizing agent ensures that ascorbic acid remains active and bioavailable for longer, maximizing its systemic effects.
Outcome: Zinc not only complements ascorbic acid but also makes its benefits more effective, particularly in areas like tissue repair, antioxidant defense, and immune support.
Antioxidant Powerhouse: Fighting the Invisible Enemy
Oxidative stress is one of the leading culprits behind chronic diseases and tissue degeneration. Zinc ascorbate tackles this problem head-on:
- Zinc: Reduces the production of reactive oxygen species (ROS) like hydrogen peroxide and stabilizes cellular membranes to prevent damage.
- Ascorbic Acid: Neutralizes free radicals and regenerates other antioxidants, creating a cascading protective effect.
Together, they form a formidable team that shields your cells from oxidative damage, reducing inflammation and preserving tissue health.
Plaque and Halitosis: Combatting the Unseen Threats
Plaque and bad breath are more than nuisances—they can be precursors to serious oral health issues. Zinc ascorbate is a game-changer in this area:
- Plaque Breakdown: Zinc actively oxidizes and breaks down existing plaque deposits while preventing new ones from forming [11].
- Odor Control: By binding sulfur compounds, zinc neutralizes bad breath, while ascorbic acid strengthens gum defenses against bacteria.
A Safe and Effective Choice
Zinc ascorbate is not only effective but also incredibly safe. While high doses of zinc or ascorbic acid alone can cause mild gastrointestinal discomfort, their combination in appropriate formulations minimizes such risks. This makes zinc ascorbate an excellent addition to oral care products, immune-boosting supplements, and wound-healing regimens.
The Future of Zinc Ascorbate: A Health Revolution
From oral health to systemic immunity, zinc ascorbate is proving to be a powerhouse ingredient. Its unique ability to combine zinc’s antimicrobial and stabilizing properties with ascorbic acid’s healing and antioxidant power makes it a versatile tool for health optimization.
Whether you’re looking to improve your oral hygiene, strengthen your immune system, or accelerate healing, zinc ascorbate offers a science-backed solution that delivers results. It’s more than just a combination of two nutrients—it’s a revolution in how we care for our health.
Zinc ascorbate is a compound that combines zinc, a vital mineral, with ascorbic acid (Vitamin C). This combination is particularly beneficial for the immune system. Zinc plays a critical role in the activation of immune cells, while Vitamin C supports the overall function of the immune system by acting as an antioxidant. Together, they work synergistically to strengthen the body’s defense against infections, reduce inflammation, and improve the immune response.
Zinc and Vitamin C work together in several ways. Zinc is essential for the proper function of immune cells such as T-cells, which are critical for immune responses. Vitamin C, on the other hand, boosts the production of white blood cells and acts as an antioxidant, protecting cells from oxidative stress. Together, they enhance the immune system’s ability to fight infections, reduce the severity of colds, and help the body recover from illness more quickly.
Zinc ascorbate is generally considered safe for pregnant women when taken in recommended doses. Zinc is crucial for fetal development, and Vitamin C is important for tissue repair and immune function. However, pregnant women should consult with a healthcare provider before starting any supplement, including zinc ascorbate, to ensure the dosage is appropriate and safe for both the mother and baby.
Zinc Ascorbate is often preferred over other zinc supplements (like zinc sulfate or zinc oxide) due to its superior absorption and lower incidence of side effects such as stomach upset or nausea. The combination of zinc and Vitamin C not only improves bioavailability but also enhances immune function, skin health, and overall recovery. Zinc Ascorbate is also gentler on the digestive system, making it a more suitable choice for those who experience discomfort with other forms of zinc.
Zinc Ascorbate is generally safe when used within the recommended doses. However, excessive intake of zinc (above 40 mg per day for adults) can lead to zinc toxicity, causing symptoms like nausea, vomiting, stomach cramps, and diarrhea. High doses of Vitamin C (more than 2,000 mg per day) can also cause gastrointestinal issues, such as diarrhea. It’s important to follow the recommended dosages and consult a healthcare provider if you have any concerns about side effects.
Yes, Zinc Ascorbate is beneficial for skin health and wound healing. Zinc supports collagen synthesis, which is essential for skin repair and maintaining skin elasticity. Vitamin C also contributes to collagen production and provides antioxidant protection, helping to reduce skin inflammation and promote healing. This makes Zinc Ascorbate an ideal supplement for those with skin issues, such as acne or wound healing problems.
Yes, Zinc Ascorbate is suitable for elderly people, particularly those with weakened immune systems. As we age, the immune system’s efficiency declines, and Zinc is vital for maintaining immune cell function. Vitamin C helps reduce oxidative stress and supports overall immune health. Zinc Ascorbate’s combination of these nutrients can help bolster immunity in older adults and reduce the risk of infections and illness.
Zinc Ascorbate is commonly used in both pharmaceutical and nutraceutical products for its immune-boosting, antioxidant, and anti-inflammatory properties. It is found in supplements designed to support immune function, promote skin health, and aid in recovery after illness or exercise. Zinc Ascorbate is also used in multivitamins and formulations that aim to address deficiencies of zinc and Vitamin C in the body.