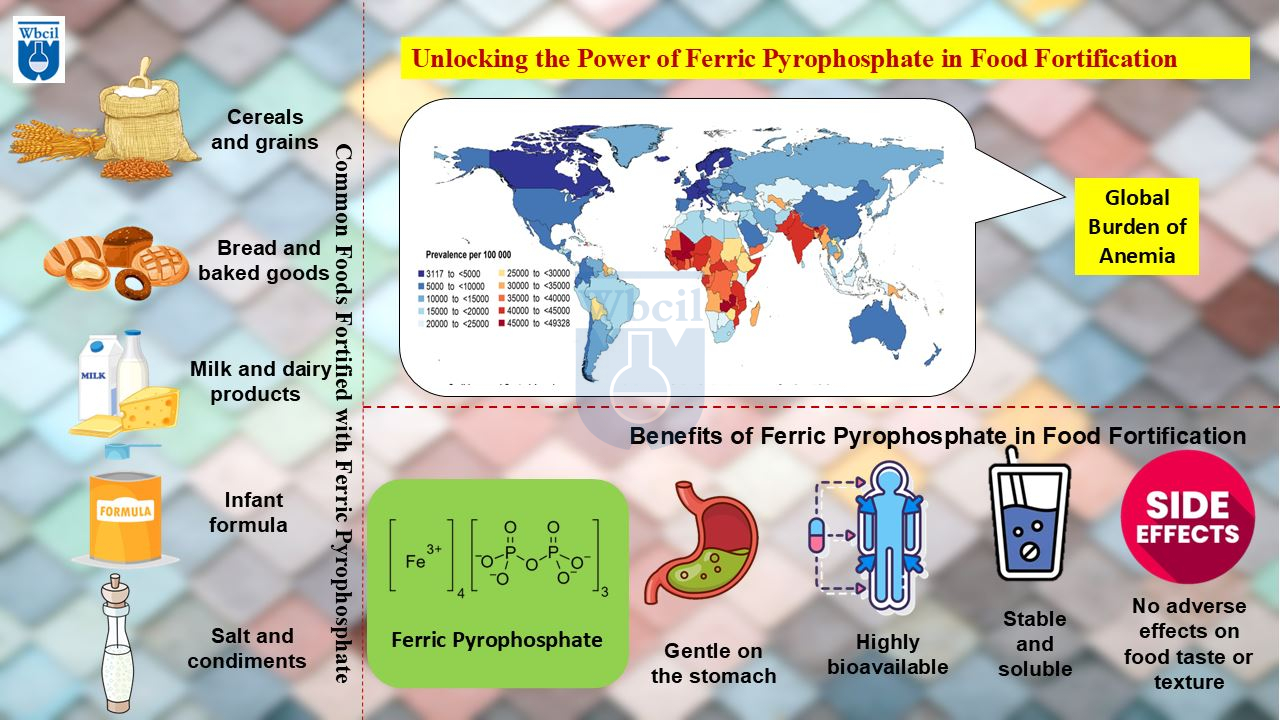
Unlocking the Power of Ferric Pyrophosphate: A Deep Dive into its Chemistry, Applications, and Benefits
Iron, the unsung hero of our red blood cells, plays a pivotal role in a multitude of bodily functions, from ferrying oxygen throughout our tissues to powering our energy production. This essential element is a cornerstone of hemoglobin, the protein within red blood cells responsible for transporting oxygen from the lungs to every part of the body. Beyond oxygen transport, iron is also a key player in numerous enzymatic reactions, DNA synthesis, and immune function. Iron deficiency, a prevalent global health issue, can manifest as debilitating fatigue, muscle weakness, cognitive impairment, and a compromised immune system, highlighting the critical importance of maintaining adequate iron levels.
Fortunately, science has provided us with effective solutions, and Ferric Pyrophosphate (Fe4P3O13) stands out as a particularly compelling one, especially in the realm of food fortification. This comprehensive exploration delves into the fascinating world of Ferric Pyrophosphate, examining its chemical makeup, diverse applications, remarkable benefits, and its crucial role in combating iron deficiency on a global scale.
What is Ferric Pyrophosphate? Unveiling the Chemical Structure and Properties
Ferric pyrophosphate is an inorganic compound composed of iron and pyrophosphate, represented by the chemical formula Fe4P3O13. This ferric pyrophosphate formula reveals its intricate structure, where four iron atoms in the ferric (Fe3+) oxidation state are bound to three pyrophosphate groups [1]. This ferric state is a key differentiator from other iron compounds like Ferrous Sulfate (FeSO4) and Ferrous Fumarate, which contain iron in the ferrous (Fe2+) state [2]. The ferric state contributes to Ferric Pyrophosphate’s enhanced stability and reduced reactivity, leading to improved bioavailability and a lower risk of adverse effects.
One of the most significant ferric pyrophosphate advantages, particularly for food fortification, is its white color. Unlike some other iron salts that can impart a dark or metallic hue to food products, Ferrous Pyrophosphate seamlessly blends into a wide array of food matrices without affecting their aesthetic appeal. This is crucial for maintaining consumer acceptance and ensuring the success of fortification programs.
Another important property is its low solubility at neutral pH. This might seem counterintuitive, but it’s actually a beneficial characteristic. The low solubility prevents Ferric Pyrophosphate from reacting prematurely with other components in the stomach, where the pH is relatively neutral. Instead, it remains intact until it reaches the more acidic environment of the small intestine, where it dissolves and becomes readily available for ferric pyrophosphate absorption. Ferric pyrophosphate soluble is a form of iron that is designed to dissolve more readily in liquids, making it suitable for certain applications like food fortification.

Uses of Ferric Pyrophosphate: A Versatile Compound
Ferric Pyrophosphate’s applications are diverse and impactful:
- Medicine: It plays a vital role in the treatment of iron deficiency anemia, a condition characterized by insufficient iron levels in the blood. It is also crucial during pregnancy to support the increased iron demands of both the mother and the developing fetus [3]. Often, it is combined with folic acid and glycine in capsule formulations to provide comprehensive nutritional support.
- Nutrition: Ferric Pyrophosphate benefits as a food fortificant, enriching staple foods like cereals, flour, rice, and dairy products with iron without altering their color or taste [4]. This is a game-changer in public health initiatives aimed at combating iron deficiency on a population-wide scale. It is also widely used in dietary supplements and nutraceuticals.
- Animal Nutrition: Ferric Pyrophosphate is an essential component of animal feed, ensuring that livestock and pets receive adequate iron for optimal growth, development, and overall health.

Benefits of Ferric Pyrophosphate: Why It’s a Preferred Choice
The widespread Ferric Pyrophosphate uses is a testament to its impressive benefits:
- High Bioavailability: The body efficiently absorbs iron from Ferric Pyrophosphate, maximizing its effectiveness in addressing iron deficiency.
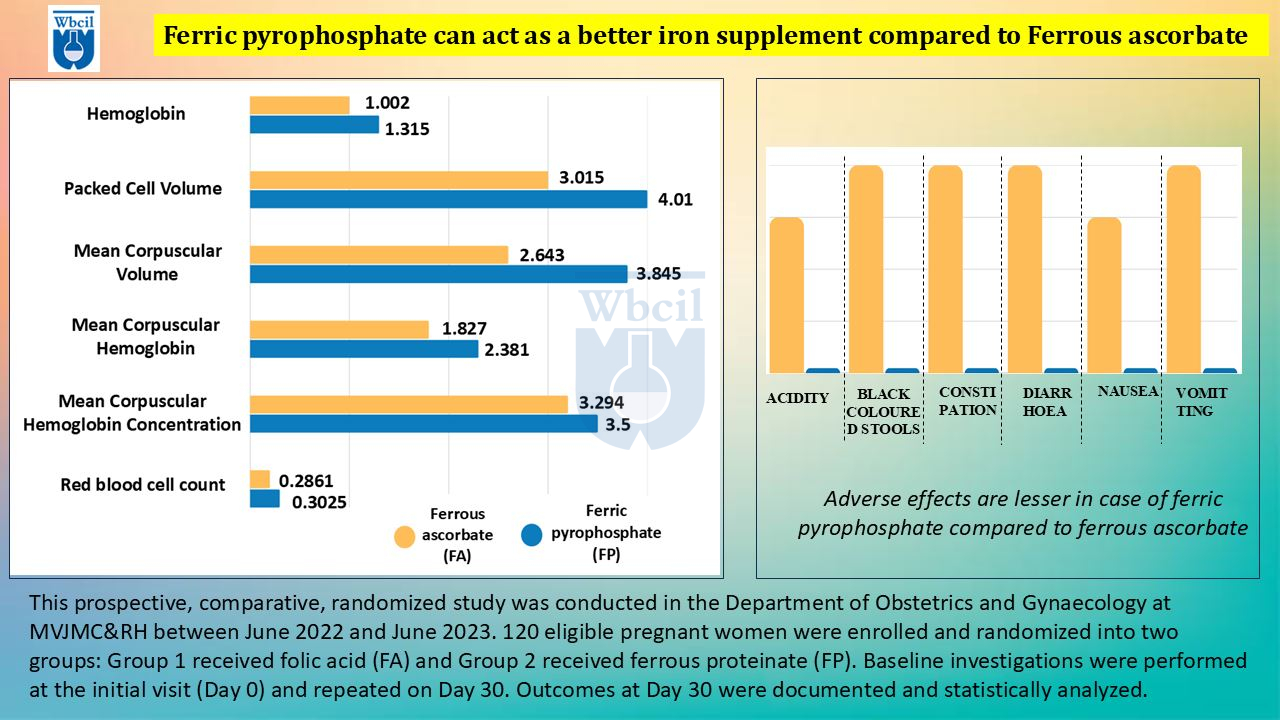
- Gentle on the Stomach: Compared to some other iron salts, Ferric Pyrophosphate is less likely to cause gastrointestinal side effects like nausea, constipation, or abdominal discomfort [5]. This makes it a well-tolerated option, even for individuals with sensitive stomachs.
- Suitable for Sensitive Populations: Its favorable safety profile makes it suitable for pregnant women, children, and the elderly, who often have increased iron needs or may be more susceptible to side effects.
- Versatility: Its wide range of applications, spanning medicine, ferric pyrophosphate in food fortification, and animal nutrition, highlights its adaptability and effectiveness in diverse settings [6].
- White Color: This is a critical advantage in food fortification, as it ensures that fortified foods retain their original appearance and color, enhancing consumer acceptance [7].
Applications in Medicine: Targeted Iron Support
- Injectable Iron Therapy: While not as commonly used as some other iron forms for injection, Ferric Pyrophosphate has been incorporated into certain injectable iron products.
- Oral Supplements: It is readily available in various oral formulations, including capsules, tablets, and syrups, providing convenient options for ferric pyrophosphate iron supplementation [8].
- Combination Therapies: Its compatibility with other nutrients allows for the development of combination therapies, such as those containing folic acid and glycine, to address multiple nutritional deficiencies concurrently [9]. Ferric pyrophosphate with folic acid is a common iron supplement often prescribed to treat iron deficiency anemia, especially during pregnancy.
Applications in Nutrition: Fortifying Health and Combating Deficiency
- Food Fortification: The Ferric Pyrophosphate in fortifying staple foods is a powerful tool in public health initiatives to combat iron deficiency on a large scale. Its white color and neutral taste make it ideal for this purpose.
- Dietary Supplements: It is a common ingredient in multivitamins and iron-specific supplements, providing a convenient way for individuals to meet their daily iron requirements.
- Functional Foods: The incorporation of Iron Pyrophosphate into health-focused food products enhances their nutritional value and contributes to overall well-being.
Ferric Pyrophosphate vs. Other Iron Compounds: A Comparative Analysis
Several iron compounds are used for supplementation and fortification, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Ferrous Sulfate, while cost-effective, is often associated with gastrointestinal side effects. Ferrous Fumarate offers slightly better tolerability but can still be harsh on the stomach [10]. Iron Bisglycinate is known for its high bioavailability and gentleness.
Iron Pyrophosphate occupies a unique position, balancing good bioavailability with excellent tolerability and possessing the crucial advantage of being white. This color neutrality makes it the ideal choice for food fortification where color preservation is paramount [11]. When comparing iron supplements, ferric pyrophosphate vs ferrous ascorbate reveals differences in absorption rates and potential gastrointestinal side effects.
Safety and Dosage Guidelines: Ensuring Safe and Effective Use
- Recommended Daily Intake: Iron requirements vary depending on factors such as age, sex, and physiological state (e.g., pregnancy, lactation). It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional to determine the appropriate daily iron intake for your individual needs.
- Ferric pyrophosphate oral dose: The ferric pyrophosphate dosage or fortified foods depends on the individual’s iron status and the specific product [12]. Always follow the instructions provided by your healthcare provider or on the product label.
- Potential Side Effects and Precautions: While generally well-tolerated, excessive iron intake can lead to side effects such as constipation, nausea, vomiting, and abdominal pain. Individuals with certain medical conditions, such as hemochromatosis (iron overload), should use iron supplements only under strict medical supervision.
Research and Innovations: The Future of Iron Supplementation
Ongoing research is exploring innovative delivery systems for Ferric Pyrophosphate, such as liposomal encapsulation, which may further enhance its ferric pyrophosphate bioavailability and minimize potential side effects. Ferric pyrophosphate citrate is a complex that combines ferric pyrophosphate with citrate, potentially influencing its solubility and bioavailability. Future trends in iron supplementation focus on personalized nutrition, targeted delivery mechanisms, and the development of more effective strategies to combat iron deficiency globally.
Conclusion: A Powerful Ally in the Fight Against Iron Deficiency
Ferric Pyrophosphate stands as a valuable and versatile tool in the fight against iron deficiency. Its high bioavailability, gentle nature, wide range of applications, and, most importantly, its white color, make it a preferred choice for food fortification and supplementation. While it offers significant benefits, it is crucial to consult with healthcare professionals before starting any iron supplementation to determine the appropriate dosage and ensure safe and effective use. Ferric Pyrophosphate holds immense promise for improving global health and nutrition, particularly in regions where iron deficiency is prevalent.
A Primarily for treating iron deficiency anemia, fortifying food products, and as a component of dietary supplements.
Ferric pyrophosphate in pregnancy is generally considered safe, but it’s crucial to consult with your doctor before taking any supplements during pregnancy.
Ferric Pyrophosphate is generally better tolerated and less likely to cause gastrointestinal side effects. Critically, it doesn’t alter the color of food.
Fortified cereals, flour, rice, and some dairy products. Always check the food label for specific information.
Usually well-tolerated, but high doses can cause mild side effects like constipation.
Yes, generally recognized as safe (GRAS).
The ferric pyrophosphate elemental iron content varies slightly depending on the specific form of Ferric Pyrophosphate. Consult product specifications for precise values.
Its white color prevents discoloration of food products, making it ideal for fortifying a wide range of foods without affecting.
Ferrous fumarate generally has higher bioavailability. Formulation can improve ferric pyrophosphate’s absorption, but individual factors and specific formulations ultimately determine iron uptake for both ferric pyrophosphate vs ferrous fumarate.
Both ferric pyrophosphate and iron bisglycinate are used as iron supplements. Iron bisglycinate generally has higher bioavailability and is better tolerated compared to ferric pyrophosphate. However, specific formulations and individual factors can influence absorption for both ferric pyrophosphate vs iron bisglycinate.