-
Product Name:
Ferric Citrate / Ferric Citrate Hydrate
-
Molecular Formula:
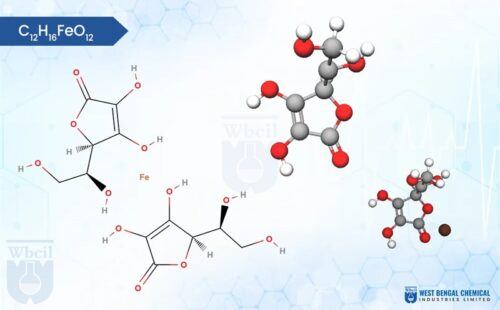
C6H5FeO7
-
Molecular Weight:
244.94 g/mol
-
CAS No.:
2338-05-8
-
HSN Code:
2918
-
CID Code:
61300
-
Shelf Life:
3 years - 20°C powder
-
ATC Code (WHO)
V03AE08
-
DrugBank ID
DB14520
-
ChemSpider ID
55239
-
UNII No.
63G354M39Z
- USP
- IUPAC Names
- Synonyms
- MSDS
USP of Ferric Citrate / Ferric Citrate Hydrate
- Ferric citrate tackles high phosphate levels, a major concern in chronic kidney disease.
- A valuable therapeutic option for managing hyperphosphatemia in chronic kidney disease (CKD) and end-stage renal disease (ESRD) patients.
- Binds excess phosphate in the gut, protecting bones and preventing complications.
- Superior iron absorption for effective delivery, addressing anemia common in kidney disease
IUPAC Names of Ferric Citrate / Ferric Citrate Hydrate
iron(3+) 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
Synonyms of Ferric Citrate / Ferric Citrate Hydrate
- FERRIC CITRATE
- Iron(III) citrate
- Iron citrate
- ferrum citricum
- ferric citrate anhydrous
- Iron citrate, FeC6H5O7
- Iron(III) citrate tribasic
- Iron(III)-citrate
- Iron (III) citrate
- ferric citrate dihydrate
- ferric citrate hydrate
- ferric citrate iron(+3) salt
- ferric citrate trihydrate
- ferric-citric acid
- iron(III) citrate
- 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, iron(3+) salt (1:1)
- Iron, (hydrogen citrato(3-))-
- Citric acid, iron salt
- Citric acid, iron(3+) salt (1:1)
- iron(iii)citrate
- iron(3+) citrate
- 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, iron salt
- 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic acid iron salt
- 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, iron(3+) salt
- Iron 2-hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylate
- Fe(3+)-citrate
- iron(3+) 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
- iron(III) 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
- Ferric citrate
- Iron(III) Citrate (Technical Grade)
- Citric acid, iron(3+) salt
- FERRICCITRATE
- 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate;iron(3+)
- (2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylato(3-)-kappa(3)O(1),O(2),O(3))iron
- Citric acid,iron(3+)salt
- 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate; iron(3+)
- Iron(III) citrate; Iron citrate
- iron(3+); 2-oxidanylpropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate
- 2338-05-8 (hydrate), 3522-50-7 (anhydrous)
- 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, iron salt (1:?)
- Ferric citrate monohydrate
- Iron(III) citrate hydrate
- Iron(III) citrate tribasic monohydrate
- ferric citrate hydrate
- 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, iron(3+) salt, hydrate (1:1:1)
- 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate;iron(3+);hydrate
- 1,2,3-Propanetricarboxylic acid, 2-hydroxy-, iron(3+) salt (1:1), monohydrate
- Iron(iii)citrate hydrate,98
- iron(III) citrate monohydrate
- IRON(3+) CITRATE HYDRATE
- iron(3+) 2-hydroxypropane-1,2,3-tricarboxylate hydrate
- 2-Hydroxy-1,2,3-propanetricarboxylic Acid, Iron(3+) Salt (1:1); Citric Acid, Iron(3+) Salt (1:1) (8CI); Fe(III)-Citrate Complex (1:1); Ferric Citrate;
MSDS of Ferric Citrate / Ferric Citrate Hydrate
Download MSDS PDF- MSDS Name: Ferric Citrate
- Product Code: FEC2022
- Relevant identified uses of the substance or mixture and uses advised against Identified uses: Laboratory chemicals, Manufacture of substances
- If inhaled: If breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing, give artificial respiration.
- In case of skin contact: Wash off with soap and plenty of water.
- In case of eye contact: Flush eyes with water as a precaution.
- If swallowed: Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse mouth with water.
- Most important symptoms and effects, both acute and delayed
The most important known symptoms and effects are described in the labelling (see section 2.2) and/or in section - Indication of any immediate medical attention and special treatment needed: No data available
- Suitable extinguishing media: Use water spray, alcohol-resistant foam, dry chemical or carbon dioxide.
- Special hazards arising from the substance or mixture: Carbon oxides, Iron oxides
- Advice for firefighters: Wear self-contained breathing apparatus for firefighting if necessary.
- Further information: No data available
- Control parameters: Not available
- Exposure controls: Not available
- Appropriate engineering controls: General industrial hygiene practice.
- Eye/face protection: Use equipment for eye protection tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or EN 166(EU).
- Skin protection: Handle with gloves. Gloves must be inspected prior to use. Use proper glove removal technique (without touching glove’s outer surface) to avoid skin contact with this product. Dispose of contaminated gloves after use in accordance with applicable laws and good laboratory practices. Wash and dry hands. The selected protective gloves have to satisfy the specifications of EU Directive 89/686/EEC and the standard EN 374 derived from it.
- Body Protection: Choose body protection in relation to its type, to the concentration and amount of dangerous substances, and to the specific work-place., The type of protective equipment must be selected according to the concentration and amount of the dangerous substance at the specific workplace.
- Respiratory protection: Respiratory protection is not required. Where protection from nuisance le (EN 143) dust masks. Use respirators and components tested and approved under appropriate government standards such as NIOSH (US) or CEN (EU).
- Control of environmental exposure: Do not let product enter drains.
- Appearance Form: Greenish brown to brown hygroscopic powder.
- Odour: No data available
- Melting point/freezing point: No data available
- Initial boiling point and boiling range: No data available
- Water solubility: Freely soluble in water
- Decomposition temperature: No data available
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Ferric-citrate
- https://whmis.org/sds/
- https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/publications/OSHA3514.pdf
- https://reachonline.eu/reach/en/annex-ii.html
- https://echa.europa.eu/registration-dossier/-/registered-dossier/29558
- https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Iron(III)_citrate
Description of Ferric Citrate / Ferric Citrate Hydrate
Ferric citrate, a complex iron supplement, comes in a variety of shades depending on its composition. It typically ranges from a greenish brown to a reddish-brown powder, with some variations like orange or even garnet red being possible. Unlike some iron supplements, ferric citrate is odorless. Notably, ferric citrate is hygroscopic, meaning it attracts moisture from the air. This can cause the powder to clump or cake over time, so proper storage in a sealed container is recommended. Texture-wise, ferric citrate is usually a fine powder, although some variations might be slightly granular. It is formed by the bonding of ferric ions (Fe3+) with citrate, a molecule derived from citric acid. This interaction creates a coordination complex, where the citrate molecule acts as a ligand, donating electron pairs to the central iron ion.
The specific structure of the complex can vary depending on the ratio of ferric ions to citrate molecules, but most commonly, a single ferric ion binds to multiple citrate ligands. This complexation with citrate enhances the solubility of iron in water compared to ferric salts like ferric chloride, making ferric citrate a bioavailable form of iron for dietary supplements and medications. Ferric citrate API can be formulated into various dosage strengths and delivery forms (e.g., tablets), catering to individual patient needs and treatment preferences.
As a leading API manufacturer, WBCIL prioritizes strict CGMP and ISO quality control measures throughout the production process. The prolonged experience from 1962 ensures consistent potency, purity, and safety in every dose of WBCIL’s Ferric citrate.
Application of Ferric Citrate / Ferric Citrate Hydrate
- Phosphate Binder: Used in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD) to manage hyperphosphatemia by reducing phosphate absorption in the intestines.
- Iron Supplement: Helps in treating iron deficiency anemia by increasing iron levels in the body.
- Food Additive: Employed as a food additive to fortify food products with iron.
- Medical Research: Utilized in various clinical studies and trials to explore its efficacy and safety in different medical conditions.
- Veterinary Medicine: used as a toxin binder
- Laboratory Reagent: Employed in laboratories for various chemical analyses and reactions.
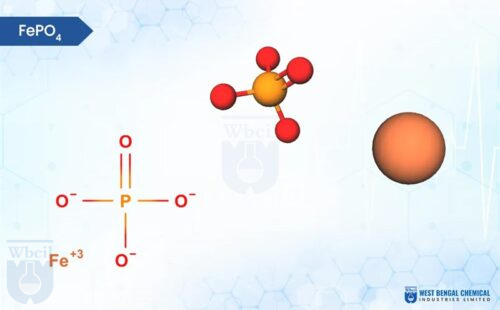
Ferric citrate is a phosphate binder with the chemical formula FeC6H5O7. It contains iron in the ferric (Fe3+) form combined with citric acid
Yes, ferric citrate reacts with dietary phosphorus in the gastrointestinal tract. The iron (Fe3+) ions in ferric citrate form insoluble complexes with phosphate (PO43-), preventing their absorption into the bloodstream. This helps to lower blood phosphorus levels.
The exact amount of phosphorus bound by a single ferric citrate tablet is 86-89 mg per 1gm FCC
Ferric citrate is used by individuals with:
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Patients with CKD who experience hyperphosphatemia (high blood phosphorus levels).
- Iron Deficiency Anemia: People who lack sufficient iron stores in their body.
Yes, ferric citrate is moderately soluble in water. This allows for its absorption in the digestive tract.
Ferric citrate API (Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient) is typically available in powder form. However, there can be some variations depending on the specific manufacturer and intended use, like, anhydrous, hydrates and granules.