-
Product Name:
Iron Sucrose
-
Molecular Formula:
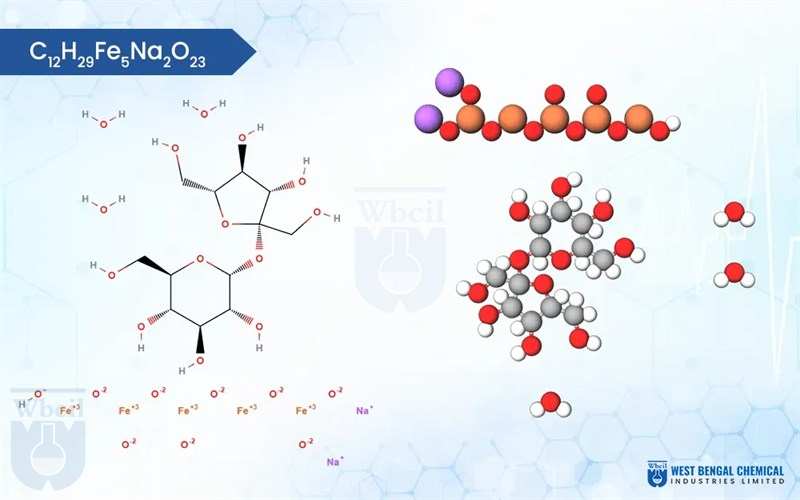
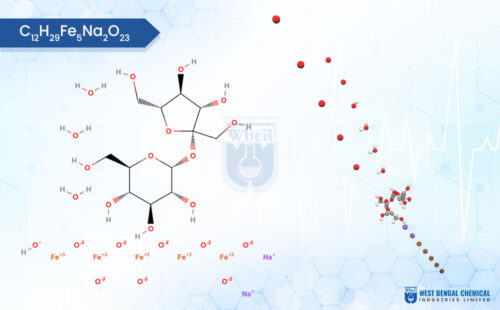
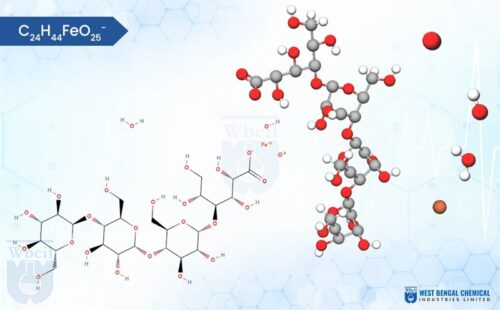
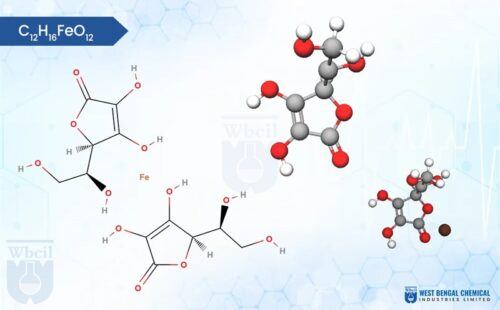
C12H29Fe5Na2O23
-
Molecular Weight:
736.1 g/mol
-
CAS No.:
8047-67-4
-
HSN Code:
30049099
-
CID Code:
91663255
-
Shelf Life:
3 years - 20°C powder
-
ATC Code (WHO)
B03AB02
-
DrugBank ID
09146
-
ChemSpider ID
32699616
-
UNII No.
FZ7NYF5N8L
- USP
- IUPAC Names
- Synonyms
- MSDS
USP of Iron Sucrose
- For patients experiencing iron deficiency, iron sucrose offers a safe and effective intravenous option for iron repletion.
- Individuals with chronic kidney disease struggling with iron absorption may benefit from the faster-acting iron delivery of iron sucrose.
- Iron sucrose minimizes the risk of allergic reactions compared to traditional iron therapies, addressing a concern for some patients.
- To determine if iron sucrose is right for you, consult with your physician for a personalized treatment plan.
IUPAC Names of Iron Sucrose
disodium;(2R,3R,4S,5S,6R)-2-[(2S,3S,4S,5R)-3,4-dihydroxy-2,5-bis(hydroxymethyl)oxolan-2-yl]oxy-6-(hydroxymethyl)oxane-3,4,5-triol;iron(3+);oxygen(2-);hydroxide;trihydrate
Synonyms of Iron Sucrose
- D-Glucaric acid, iron(2+) salt (1:1)
- Ferri Saccharate
- ferri-saccharate
- ferric oxide, saccharated
- ferric saccharate
- iron oxide (saccharated)
- Iron Saccharate
- iron sucrose
- iron(III)-hydroxide sucrose complex
- iron-saccharate
- Saccharated Ferric Oxide
- Saccharated iron
- Saccharated iron oxide
- Sucroferric oxyhydroxide
- Saccharated ferric oxide
MSDS of Iron Sucrose
Download MSDS PDF- Product Name: Iron Sucrose
- Company Identification: IRS4580
- Relevant identified uses of the substance or mixture and uses advised against: An iron replacement product indicated for the treatment of iron deficiency anemia in patients with chronic kidney disease (CKD), Industrial and scientific research uses.
- General advice: Consult a physician. Show this safety data sheet to the doctor.
- If inhaled: If breathed in, move person into fresh air. If not breathing give artificial respiration.
- In case of skin & eye contact: In case of eye, rinse with plenty of water, and in case of skin, wash with plenty of soap and water.
- If swallowed: Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Rinse Mouth with water.
- Flammability of the Product: Non-flammable.
- Auto-Ignition Temperature: Not applicable.
- Flash Points: Not applicable.
- Flammable Limits: Not applicable.
- Products of Combustion: Not available.
- Fire Hazards in Presence of Various Substances: Not applicable.
- Explosion Hazards in Presence of Various Substances:
Risks of explosion of the product in presence of mechanical impact: Not available.
Risks of explosion of the product in presence of static discharge: Not available. - Fire Fighting Media and Instructions: Wear a self-contained breathing apparatus and chemical protective clothing.
- Special Remarks on Fire Hazards: Toxic fumes.
- Special Remarks on Explosion Hazards: Do not inhale explosion and combustion gases. Collect contaminated fire extinguishing water separately. This must not be discharged into drains. Move undamaged containers from immediate hazard area if it can be done safely.
- Engineering Controls: Use process enclosures, local exhaust ventilation, or other engineering controls to keep airborne levels below recommended exposure limits. If user operations generate dust, fume or mist, use ventilation to keep exposure to airborne contaminants below the exposure limit.
- Personal Protection: Safety glasses. Lab coat. Dust respirator. Be sure to use an approved / certified respirator or equivalent. Gloves.
- Personal Protection in Case of a Large Spill: Splash goggles. Full suit. Dust respirator. Boots. Gloves. A self-contained breathing apparatus should be used to avoid inhalation of the product. Suggested protective clothing might not be sufficient; consult a specialist BEFORE handling this product.
- Exposure Limits: TWA: 1 (mg/m3) from ACG IH Consult local authorities for acceptable exposure limits.
- Appearance: Powder
- Odor: Not available.
- Taste: Not available.
- Color: Deep Brown
- Solubility: Soluble in warm Water
- Specific Gravity: Not available
- Vapour Pressure (mm Hg): Not applicable
- Vapour Density (Air = 1): Not available
- Molecular Weight: 736.06 g/mol
- pH: 9.5 – 11.5
Description of Iron Sucrose
Iron sucrose is a complex molecule used to replenish iron stores in individuals with deficiency, particularly those with chronic kidney disease. Unlike oral iron supplements, iron sucrose is administered intravenously. Physically, it appears as a brown to reddish-brown sterile solution and is odorless. Interestingly, iron sucrose is hygroscopic, meaning it readily absorbs moisture from the surrounding environment. This property necessitates storage in airtight containers. While the exact texture of the solution itself isn’t described, being delivered intravenously means it has a viscosity suitable for injection through a needle.
Chemically, iron sucrose is a coordination complex. It features a core of five iron(III) ions surrounded by hydroxide groups and complexed with sucrose, a common sugar molecule. This unique structure allows for controlled release of iron into the bloodstream, minimizing side effects often associated with oral iron supplementation. As a leading API manufacturer, WBCIL prioritizes strict CGMP and ISO quality control measures throughout the production process. The prolonged experience from 1962 ensures consistent potency, purity, and safety in every dose of WBCIL’s iron sucrose.
Application of Iron Sucrose
Pharmaceutical Industry
Intravenous Iron Therapy
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Used to treat iron deficiency anemia in patients with CKD, including those on hemodialysis and peritoneal dialysis.
- Postpartum Anemia: Administered to women experiencing iron deficiency anemia after childbirth.
- Cancer Patients: Provided to cancer patients undergoing chemotherapy who experience anemia.
- Gastrointestinal Disorders: Used for patients with inflammatory bowel disease or other conditions that impair iron absorption.
- Surgical Patients: Given to patients pre- and post-operatively to manage anemia and improve recovery.
Perinatal Care
- Pregnancy: Administered to pregnant women to prevent and treat iron deficiency anemia, ensuring proper maternal and fetal health.
- Postpartum Period: Used to replenish iron stores and address anemia following childbirth.
Hospital and Clinical Settings
- Anemia Management: Utilized in hospitals for rapid correction of iron deficiency anemia in various patient populations, including those with heart failure and chronic blood loss.
- Preoperative Preparation: Given to patients prior to major surgeries to correct anemia and reduce the need for blood transfusions.
Long-Term Care Facilities
Elderly Care: Used to manage iron deficiency anemia in elderly patients residing in long-term care facilities who may have limited dietary intake or chronic illnesses affecting iron absorption.
Hemodialysis Centers
Routine Iron Supplementation: Regularly administered to hemodialysis patients to maintain adequate iron levels and support erythropoiesis, reducing the need for blood transfusions.
Iron sucrose is an intravenous iron therapy commonly used for:
- Iron Deficiency Anemia (IDA): Effective in treating anemia caused by iron deficiency, especially in patients who cannot tolerate oral iron supplements.
- Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD): Essential for managing anemia in CKD patients, particularly those undergoing dialysis.
- Pregnancy: Used to treat iron deficiency anemia in pregnant women to ensure maternal and fetal health.
- Post-Surgical Recovery: Helps in replenishing iron stores after significant blood loss during surgeries.
- Cancer-related Anemia: Beneficial for patients experiencing anemia due to chemotherapy or radiation therapy.
Side effects of Iron Sucrose:
The side effects of iron sucrose can vary in severity and frequency.
- Hypotension (low blood pressure)
- Nausea
- Vomiting
- Headaches
- Dizziness
- Muscle cramps
Iron sucrose is an iron replacement medication delivered intravenously (IV) to treat iron deficiency anemia, especially in chronic kidney disease (CKD) patients. It replenishes iron stores by delivering iron sucrose particles into the bloodstream, which are then taken up by cells.
Iron sucrose bypasses the digestive system, avoiding issues like poor absorption and gastrointestinal side effects common with oral iron.
Treatment duration varies depending on iron stores repletion and can involve multiple doses.
Iron sucrose can decrease the absorption of certain antibiotics, antifungal medications, and bone-modifying drugs. It’s crucial to inform your doctor about all medications you take.
Iron sucrose is generally well-tolerated in patients with CKD, unlike some oral iron supplements that can worsen kidney function.
Blood tests to measure iron levels (hemoglobin, ferritin) are used to assess the effectiveness of iron sucrose therapy.