-
Product Name:
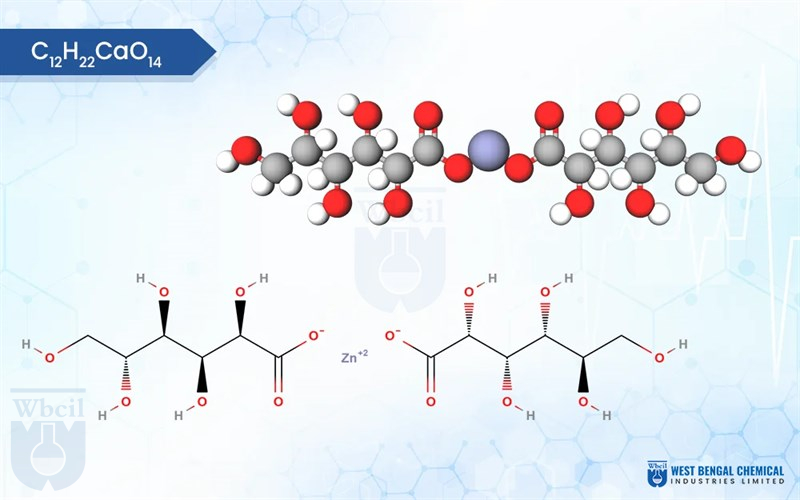
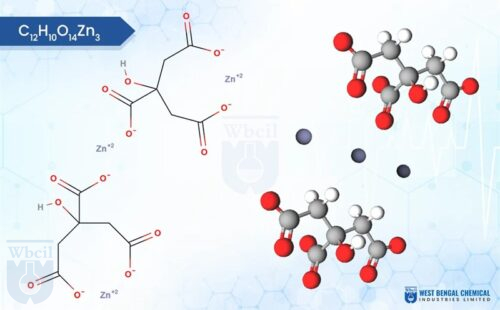
Zinc Gluconate
-
Molecular Formula:
C12H22O14Zn.xH2O
-
Molecular Weight:
455.7 + xH2O g/mol
-
CAS No.:
4468-02-4
-
HSN Code:
29224990
-
CID Code:
443445
-
Shelf Life:
3 years - 20°C powder
-
ATC Code (WHO)
A12CB02
-
DrugBank ID
DB11248
-
ChemSpider ID
391659
-
UNII No.
U6WSN5SQ1Z
- USP
- IUPAC Names
- Synonyms
- MSDS
USP of Zinc Gluconate
- Zinc gluconate potentially treats zinc deficiency.
- Zinc gluconate improves immune function and heart health.
IUPAC Names of Zinc Gluconate
zinc;(2R,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoate
Synonyms of Zinc Gluconate
- ZINC GLUCONATE
- 4468-02-4
- Zincum gluconicum
- Zinc D-gluconate (1:2)
- Bis(D-gluconato-O1,O2) zinc
- U6WSN5SQ1Z
- Zinc gluconate hydrate
- Gluconic Acid Zinc(II) Salt
- UNII-U6WSN5SQ1Z
- Zinc(II) (2R,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoate
- Bis(D-gluconato-O(sup 1),O(sup 2))zinc
- Zinc, bis(D-gluconato-O1,O2)-
- Zinc bis(D-gluconato-O1,O2)
- Zinc, bis(D-gluconato-O(sup 1),O(sup 2))-
- Zinc Glucocate
- Bis(D-gluconato-O1,O2) zinc (2) zinc D-gluconate (1:2)
- Zinc, bis(D-agluconato-aI masculineO1,aI masculineO2)a-a, (T-a4)a-
- zinc (2R,3S,4R,5R)-2,3,4,5,6-pentahydroxyhexanoate;Zinc gluconate hydrate
MSDS of Zinc Gluconate
Download MSDS PDF- MSDS Name: Zinc Gluconate USP
- Product Code: ZGLUS97
- Relevant identified uses of the substance or mixture and uses advised against: Food Additives in Nutrients Food industry: supplement
- Inhalation: Move exposed person to fresh air. If not breathing, seek immediate medical attention. If breathing is irregular or if respiratory arrest occurs, provide artificial respiration or oxygen by trained personnel and seek medical attention.
- Ingestion: Do not induce vomiting unless directed to do so by medical personnel. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Seek medical attention.
- Skin Contact: Remove contaminated clothing and shoes and immediately flush skin with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes. Wash clothing before reuse. Clean shoes thoroughly before reuse. If irritation persists, seek medical attention.
- Eye Contact: Check for and remove any contact lenses. Immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes, occasionally lifting the upper and lower eyelids. Seek immediate medical attention.
- Flammability of the Product: May be combustible at high temperature.
- Auto-Ignition Temperature: Not available.
- Flash Points: Not available.
- Flammable Limits: These products are carbon oxides (CO, CO2), nitrogen oxides (NO, NO2…). Some metallic oxides.
- Products of Combustion: Slightly flammable to flammable in presence of heat. Non-flammable in presence of shocks.
- Fire Hazards in Presence of Various Substances: Slightly explosive in presence of open flames and sparks. Non-explosive in presence of shocks.
- Fire Fighting Media and Instructions:
SMALL FIRE: Use DRY chemical powder.
LARGE FIRE: Use water spray, fog or foam. Do not use water jet. - Special Remarks on Fire Hazards: Fire is possible at elevated temperatures.
- Special Remarks on Explosion Hazards: Fine dust dispersed in air in sufficient concentrations, and in the presences of an ignition source is a potential dust explosion hazard.
- Engineering Controls: Use process enclosures, local exhaust ventilation, or other engineering controls to keep airborne levels below Recommended exposure limits. If user operations generate dust, fume or mist, use ventilation to keep exposure to airborne contaminants below the exposure limit.
- Personal Protection: Safety glasses. Lab coat. Dust respirator. Be sure to use an approved/certified respirator or equivalent. Gloves.
- Personal Protection in Case of a Large Spill: Splash goggles. Full suit. Dust respirator. Boots. Gloves. A self-contained breathing apparatus should be used to avoid inhalation of the product. Suggested protective clothing might not be sufficient; consult a specialist BEFORE handling this product.
- Exposure Limits: Not available.
- Appearance Form: White or practically white powder or granules
- pH (of 1% w/v aqueous suspension): 5.5 – 7.5
- Melting point/freezing point: No data available
- Initial boiling point and boiling range: No data available
- Sublimation Temperature: No data available
- Other safety information: No data available
- https://whmis.org/sds/
- https://www.osha.gov/sites/default/files/publications/OSHA3514.pdf
- https://reachonline.eu/reach/en/annex-ii.html
- https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/npg/
- https://echa.europa.eu/da/substance-information/-/substanceinfo/100.022.489
- https://echa.europa.eu/da/registration-dossier/-/registered-dossier/24253/4/5
- https://pubchem.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/compound/Zinc-Gluconate#section=2D-Structure
- https://www.chemicalbook.com/ChemicalProductProperty_EN_CB6728315.htm
Description of Zinc Gluconate
Zinc gluconate, a popular form of zinc supplement, boasts unique physical and chemical properties. Typically appearing as white, odourless crystals or a fine powder, it offers a slight advantage over other zinc salts – it’s not hygroscopic. This means it won’t readily absorb moisture from the air, making it easier to handle and store. Texture-wise, zinc gluconate can range from slightly gritty to smooth depending on the particle size. Scientifically, zinc gluconate is classified as an ionic compound.
It forms when zinc (Zn2+) cations bond with gluconate anions (C6H11O73-). Each zinc ion is linked to two gluconate molecules. This chemical structure offers a gentler delivery of zinc compared to some other forms, potentially reducing stomach upset. As a leading API manufacturer, WBCIL prioritizes strict CGMP and ISO quality control measures throughout the production process. The prolonged experience from 1962 ensures consistent potency, purity, and safety in every dose of WBCIL’s zinc gluconate.
Application of Zinc Gluconate
Pharmaceutical Industry
- Nutritional supplements: Zinc gluconate can be formulated into tablets, capsules, or liquid supplements to treat zinc deficiency.
- Immune support products: It can be used in supplements designed to boost immune function, especially during cold and flu seasons.
- Cardiovascular health supplements: Zinc gluconate can be incorporated into heart health formulations.
Nutraceutical Industry
- Functional foods: Zinc gluconate can be added to fortified foods and beverages to enhance their nutritional value and provide immune support.
- Sports nutrition: It can be used in pre-workout or recovery supplements to support immune function and overall health in athletes.
Healthcare Industry
- Clinical nutrition: Zinc gluconate can be used in nutritional formulations for patients with compromised immune systems or those at risk of zinc deficiency.
- Geriatric care products: It can be incorporated into supplements designed specifically for elderly individuals to support their immune function and heart health.