Calcium Dobesilate- A Comprehensive Guide to Vascular Health
What is Calcium dobesilate?
Our bodies are intricate networks of highways, with blood vessels carrying vital supplies throughout. But what happens when these highways get congested or damaged? This is where circulation comes in, and sometimes, it needs a little boost. That’s where calcium dobesilate steps onto the scene.
Beyond Calcium: A Multitasking Marvel
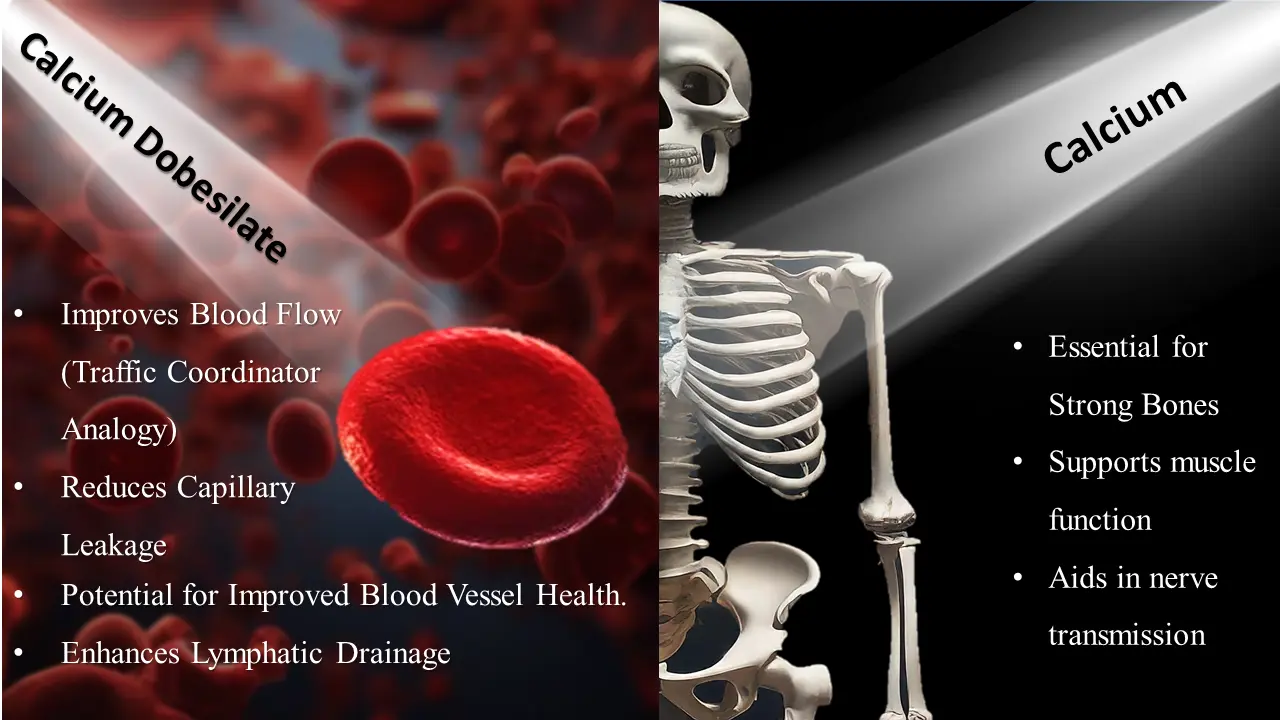
Calcium, we all know, is essential for strong bones. But calcium dobesilate is a different beast altogether. This medication acts like a traffic coordinator for your blood cells, particularly in the veins. By improving their flexibility and reducing clumping, C12H10CaO10S2 helps blood flow smoothly, preventing unwanted traffic jams.
Classified as a vasoprotective agent, it has gained recognition for its potential to improve blood vessel health. C12H10CaO10S2 is a medication used to treat hemorrhoids (piles) and varicose veins. Calcium Dobesilate works by reducing capillary leakage, thickening blood, and enhancing fluid removal through the lymphatic system.
Calcium Dobesilate chemical properties:
Calcium dobesilate is a calcium salt of dobesilic acid (2,5-Dihydroxy Benzene Sulfonic acid, calcium salt). It exists in two forms
- Free Acid Form: This is the core molecule, dobesilic acid, combined with a calcium ion (Ca+2).
Chemical Formula: C12H10CaO10S2 1 - calcium dobesilate monohydrate Form: This form has one molecule of water (H2O) attached to the free acid form.
Chemical Formula: C12H12CaO11S2 2

Calcium Dobesilate benefits:
Calcium dobesilate is commonly prescribed to treat conditions related to weak or damaged blood vessels, including:
Diabetic retinopathy:
Diabetic retinopathy, a microvascular complication of diabetes, disrupts the blood-retinal barrier leading to leakage and haemorrhage within the retina 3.
C12H10CaO10S2 for diabetic retinopathy, with its potential to improve vascular health by reducing capillary fragility and permeability, has emerged as a therapeutic candidate for this condition 4. It effectively relieves haemorrhoid symptoms by reducing inflammation, improving blood circulation, and promoting healing in the affected area 5.
Calcium dobesilate for varicose veins:
C12H10CaO10S2 has demonstrated superior efficacy compared to placebo in alleviating certain chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) symptoms, with more pronounced benefits observed in patients with severe CVI. 6 7. Calcium dobesilate has emerged as a potential therapeutic agent for CVI, with studies suggesting its ability to improve blood flow and reduce leakage from weakened vessels 8 9.
Hemorrhoids (piles):
Internal haemorrhoids, characterized by dilated and tortuous veins in the anal canal and rectum 7 8 9, can cause significant discomfort. Calcium Dobesilate for haemorrhoids effectively relieves symptoms by reducing inflammation, improving blood circulation, and promoting healing in the affected area. 10.
Calcium dobesilate helps strengthen blood vessels, reducing fluid leakage and swelling in tissues. The use of 2,5-Dihydroxybenzenesulfonic acid calcium salt for piles & fistula is being explored as a potential treatment to improve symptoms and promote healing 11 12.
Mechanism of Action:
Understanding calcium dobesilate’s pharmacokinetics, which refers to how the body absorbs, distributes, metabolizes, and excretes the medication, is crucial for optimal treatment 13. While the exact mechanism of action of calcium dobesilate is still being explored, research suggests it may influence various pathways to improve blood vessel health 14 15.
Reduced Capillary Permeability:
The primary mechanism of action for 2,5-Dihydroxybenzenesulfonic acid calcium salt is believed to be its effect on capillary wall structure, particularly the basement membrane. This scaffold-like layer provides crucial support and stability to blood vessels 16 17. Calcium dobesilate appears to interact with the basement membrane in two ways:
Stabilization of collagen chains:
Collagen is a major structural component of the basement membrane 18. By stabilizing these collagen chains, calcium dobesilate may reinforce the overall integrity of the capillary wall 19 20.
Interaction with biochemical mediators:
These molecules regulate capillary permeability, influencing how much fluid leaks out of the vessels 21. Calcium dobesilate might influence the activity of these mediators, leading to a reduction in leakage 22 23.
Improved Blood Flow
Reduced Blood Viscosity:
While not a true blood thinner, calcium dobesilate may slightly decrease whole blood viscosity, particularly at low shear rates relevant to venous flow 24. This could improve blood flow within hemorrhoidal veins.
o Enhanced Nitric Oxide Production: Recent research suggests calcium dobesilate might stimulate the production of nitric oxide (NO) in the endothelium, the inner lining of blood vessels 25 26. NO acts as a vasodilator, promoting relaxation of blood vessel walls and potentially improving circulation in hemorrhoidal tissue 27.
Possible Anti-inflammatory Effects:
Emerging evidence suggests calcium dobesilate possesses anti-inflammatory properties, potentially offering therapeutic benefits in chronic venous insufficiency (CVI) and hemorrhoids 14.
Calcium Dobesilate Medication:
Calcium Dobesilate applications in medicine are being explored for various conditions affecting blood vessel health. Calcium Dobesilate tablets are commonly used to treat hemorrhoids and varicose veins by improving blood circulation and reducing inflammation 28. The price of Calcium Dobesilate tablets can vary based on brand, dosage, and location.
Calcium Dobesilate uses:
- Calcium Dobesilate is categorized as a pregnancy category C drug, meaning its potential benefits may outweigh risks in certain cases, but use during pregnancy should only occur under strict medical supervision.
- Calcium Dobesilate can help improve the appearance of spider veins by strengthening blood vessel walls and reducing inflammation 29.
Calcium Dobesilate is not recommended for paediatric use due to insufficient safety and efficacy data. - Calcium dobesilate and hypertension remain a topic of research, with some studies exploring its potential to lower blood pressure in certain circumstances. The safety and efficacy of calcium dobesilate in lactation require further investigation.
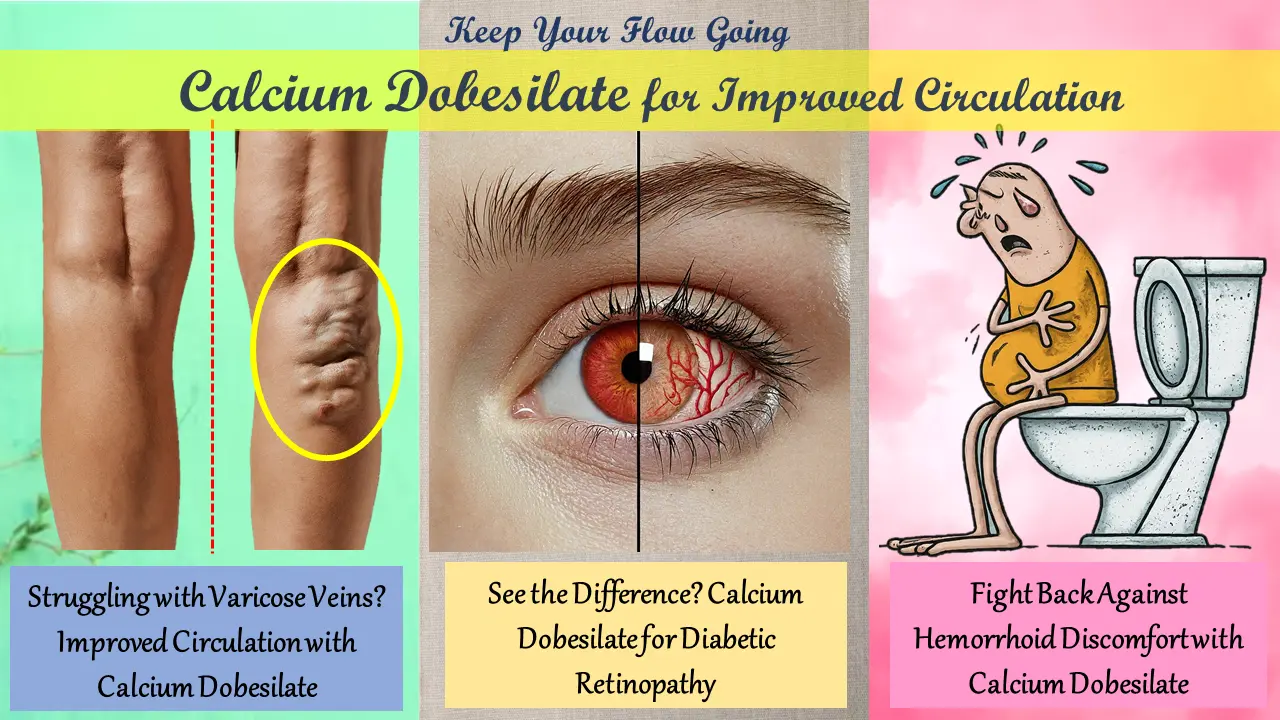
Calcium Dobesilate indication
- Calcium dobesilate and docusate sodium capsules are used in combination to treat constipation and potentially improve symptoms associated with hemorrhoids 30.
- Calcium dobesilate and docusate sodium capsules are used in combination to treat constipation and potentially improve symptoms associated with hemorrhoids.
- Calcium dobesilate and lignocaine hydrochloride ointment is a topical medication used to potentially alleviate discomfort and inflammation associated with hemorrhoids.
- Calcium dobesilate and euphorbia prostrata are sometimes combined in medications to potentially improve blood vessel health and alleviate symptoms associated with hemorrhoids.
- The combination of calcium dobesilate and troxerutin is being investigated for its potential to improve microcirculation and manage symptoms related to chronic venous insufficiency.
- Calcium dobesilate and diosmin are sometimes combined in formulations to potentially improve blood vessel function and reduce symptoms associated with chronic venous insufficiency (CVI).
Calcium Dobesilate dosage and Administration:
Calcium dobesilate is typically administered orally, available in tablet or capsule form. For optimal absorption, it’s recommended to take it with meals 31. The typical adult dosage for Calcium Dobesilate is 0.5 to 1 gram per day, divided into multiple doses. The specific dosage and treatment duration will vary depending on the treated condition and individual patient factors. Always adhere to your physician’s prescribed regimen 32.
Proper application of calcium dobesilate gel involves cleaning the affected area, applying a small amount, and gently massaging it in as directed by the product label or healthcare provider. Finding information on specific calcium dobesilate brands may require consulting a healthcare professional or pharmacist due to regional availability and potential prescription requirements.
Calcium Dobesilate Side effects
It’s important to be aware of calcium dobesilate contraindications, such as known allergies to the medication or its components, pregnancy, and breastfeeding, before starting treatment.
Calcium Dobesilate can cause side effects like fever, skin rashes, joint pain, digestive issues, and in rare cases, a low white blood cell count. It’s advisable to refrain from alcohol consumption while taking Calcium Dobesilate.
Comparative Analysis of Calcium Dobesilate with Other Calcium Compounds and Medications
- Calcium Dobesilate vs Diosmin: Calcium dobesilate and diosmin both enhance vascular health, but dobesilate primarily reduces capillary permeability, while diosmin improves vein tone and reduces inflammation.
- Calcium Dobesilate vs Calcium Carbonate: Calcium dobesilate is used to improve blood vessel health, whereas calcium carbonate is a dietary supplement for bone health and a common antacid.
- Calcium Dobesilate vs Nifedipine: Calcium dobesilate enhances blood vessel integrity and circulation, while nifedipine is a calcium channel blocker used primarily to treat hypertension and angina.
- Calcium Hydroxide vs Calcium Dobesilate: Calcium hydroxide is commonly used in dental applications and as a construction material, while calcium dobesilate is a medication aimed at improving blood vessel health.
- Calcium Gluconate vs Calcium Dobesilate: Calcium gluconate is primarily used to treat calcium deficiencies, whereas calcium dobesilate is utilized for its vascular protective properties.
- Calcium Oxide vs Calcium Dobesilate: Calcium oxide, or quicklime, is used in industrial processes, while calcium dobesilate is a pharmaceutical agent improving blood vessel health and circulation.
Conclusion:
Calcium dobesilate pharmacology shows promise for improving microvascular circulation and reducing capillary fragility. While its mechanism requires further investigation, its potential benefits for vascular health, particularly in diabetic patients with microvascular complications, warrant continued research and clinical trials.
Calcium dobesilate helps in treating hemorrhoids by reducing inflammation, improving blood circulation, and strengthening the blood vessels, which can alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
Calcium dobesilate is not typically used to treat fissures directly. Its role is primarily in improving blood vessel health, which can indirectly support healing by enhancing circulation and reducing inflammation in the affected area.
The onset of action for calcium dobesilate can vary depending on the condition being treated. Patients may start noticing improvements within a few days to a few weeks of consistent use, but full therapeutic effects may take several weeks.
Calcium dobesilate is not commonly associated with causing constipation. However, side effects can vary among individuals, and any new or worsening symptoms should be discussed with a healthcare provider.
To apply calcium dobesilate cream, clean and dry the affected area, then apply a small amount of the cream to the area as directed by your healthcare provider. Gently massage it in until fully absorbed. Follow the specific instructions provided with the medication.
Calcium dobesilate is generally considered safe when used as directed by a healthcare professional. However, it can cause side effects such as gastrointestinal disturbances, skin reactions, and rarely, changes in blood cell counts. Always consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new medication.
Calcium dobesilate is primarily used as a vasoprotective agent to improve blood vessel health. It is effective in treating conditions like diabetic retinopathy, hemorrhoids, and varicose veins by reducing capillary permeability and improving microcirculation.
In dermatology, calcium dobesilate may be used to improve microcirculation and reduce symptoms related to chronic venous insufficiency, such as varicose veins and venous ulcers, by enhancing blood flow and reducing inflammation.
Calcium dobesilate can interact with other medications, though specific interactions are not well-documented. It’s important to inform your healthcare provider of all medications and supplements you are taking to avoid potential interactions.