Sucroferric Oxyhydroxide: A Breakthrough in Hyperphosphatemia Treatment
Hyperphosphatemia, a common and serious complication of Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD), especially in dialysis patients, poses a significant threat to overall health. Elevated phosphate levels can trigger a cascade of adverse effects, including cardiovascular problems, debilitating bone disorders, and a decline in overall well-being. Fortunately, advancements in medical science have led to innovative solutions.
Sucroferric oxyhydroxide, a cutting-edge iron-based phosphate binder, is revolutionizing hyperphosphatemia management in CKD patients. This blog delves into the mechanisms, benefits, clinical evidence, and comparative advantages of sucroferric oxyhydroxide, highlighting its potential to improve the lives of those affected by this challenging condition.
Understanding Hyperphosphatemia and Its Risks
Hyperphosphatemia occurs when excess phosphorus accumulates in the bloodstream due to impaired kidney function. Healthy kidneys efficiently filter out phosphorus, maintaining a delicate balance. However, in CKD, this filtration process is compromised, leading to phosphate buildup. The consequences of hyperphosphatemia are far-reaching:
- Cardiovascular Diseases: High phosphate levels contribute to vascular calcification, increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
- Vascular Calcification: Phosphate deposits in blood vessels stiffen them, hindering blood flow and exacerbating cardiovascular issues.
- Bone and Mineral Disorders (Renal Osteodystrophy): Hyperphosphatemia disrupts calcium and vitamin D metabolism, weakening bones and increasing fracture risk.
- Increased Mortality Risk: Studies have shown a strong correlation between elevated phosphate levels and increased mortality in dialysis patients.
Dietary restrictions alone are often insufficient to manage phosphate levels, necessitating the use of phosphate binders.

What Is Sucroferric Oxyhydroxide?
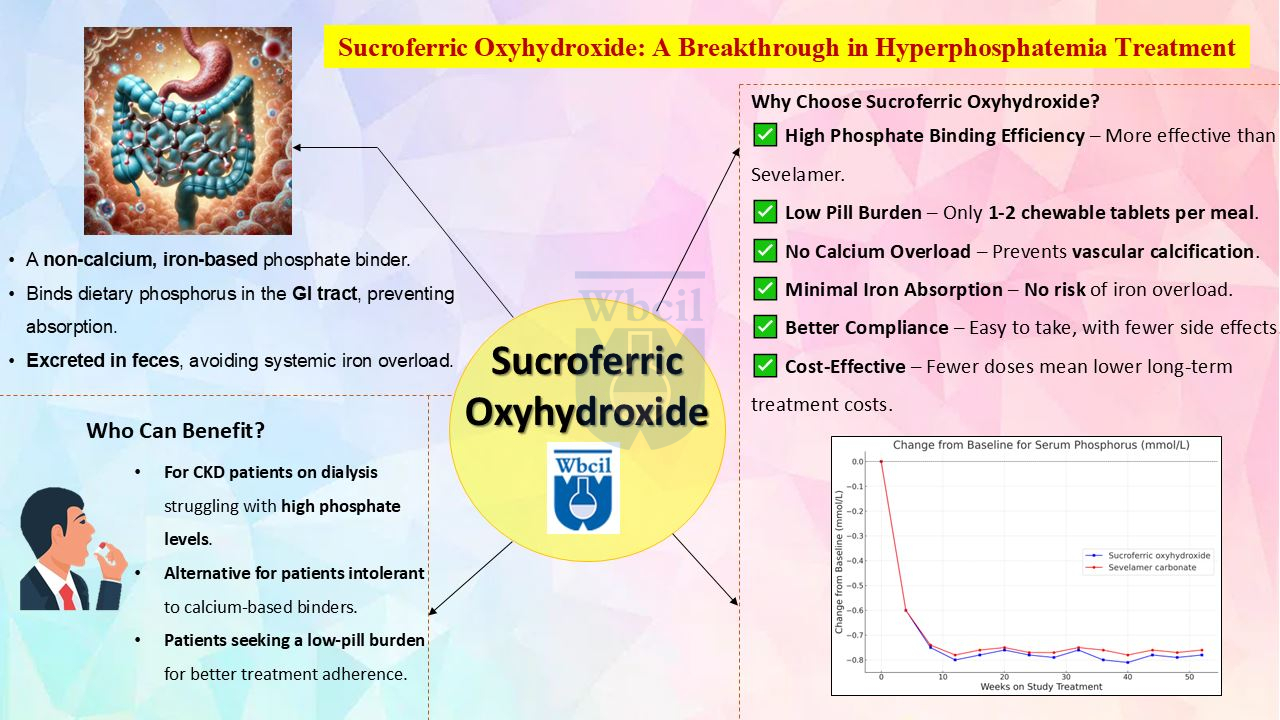
Sucroferric oxyhydroxide is a non calcium, iron based phosphate binder specifically designed for managing dialysis phosphate management in CKD patients. Its mechanism of action involves binding dietary phosphorus in the gastrointestinal tract, forming insoluble compounds that are then excreted in the feces. Crucially, unlike calcium-based binders, sucroferric oxyhydroxide does not contribute to vascular calcification. Key features include high phosphate-binding efficiency, minimal systemic iron absorption, and a lower pill burden compared to traditional binders.
How Does Sucroferric Oxyhydroxide Work?
The effectiveness of sucroferric oxyhydroxide lies in its unique iron based binding mechanism. Within the gastrointestinal tract, the iron in the compound forms a stable complex with dietary phosphorus, effectively reducing phosphate absorption into the bloodstream. A significant advantage is the minimal systemic iron absorption, which mitigates the risk of iron overload, a common concern with other iron-based medications. Compared to other phosphate binders:
- Calcium-based binders: Pose a risk of hypercalcemia and vascular calcification.
- Aluminum-based binders: Carry toxicity concerns.
- Lanthanum carbonate: While a non calcium phosphate binder, it often requires more frequent dosing.
- Sevelamer: Effective but necessitates multiple tablets daily.
Clinical Benefits of Sucroferric Oxyhydroxide
Clinical trials have demonstrated the significant benefits of sucroferric oxyhydroxide:
- High Phosphate-Binding Capacity: It effectively reduces serum phosphate levels in dialysis patients, often proving more potent than sevelamer or calcium-based binders with fewer tablets.
- Lower Pill Burden: The need for only one or two chewable tablets per meal improves patient compliance and adherence to treatment, leading to better renal phosphate control.
- Reduced Risk of Hypercalcemia: Being a non calcium phosphate binder, it eliminates the risk of excess calcium deposits in blood vessels, a concern with calcium-based binders.
- Gastrointestinal Tolerability: Common side effects are generally mild (e.g., diarrhea, dark stools) and rarely require discontinuation of treatment.
- Cost-Effectiveness: The high efficiency of saved cost of sucroferric oxyhydroxide treatment can translate to cost savings over time due to the reduced need for multiple doses compared to other treatments.
Sucroferric oxyhydroxide effectively lowers serum phosphorus in dialysis patients. A 52-week study (Figure 1) showed sucroferric oxyhydroxide vs sevelamer carbonate significantly reduced phosphorus from baseline, with the former appearing to maintain slightly lower levels from week 8 onward. This suggests a potential benefit of sucroferric oxyhydroxide for long-term hyperphosphatemia management, though further analysis is needed to confirm between-group differences.
Who Should Use Sucroferric Oxyhydroxide?
Sucroferric oxyhydroxide is an ideal option for:
- CKD patients on dialysis struggling with hyperphosphatemia in kidney disease.
- Patients intolerant to calcium-based or aluminum-based phosphate binders.
- Individuals seeking a low-pill burden treatment to improve adherence.
It should be avoided by patients with severe iron overload disorders (e.g., hemochromatosis) and those with known hypersensitivity to iron compounds. Sucroferric oxyhydroxide dosage for dialysis patients is typically 500mg chewable tablets taken with meals, with adjustments made by a physician based on individual phosphate levels.
Common Questions About Sucroferric Oxyhydroxide
- How quickly does it lower phosphate levels? Patients can typically expect to see a noticeable reduction in phosphate levels within 2-4 weeks of consistent use.
- Can it be taken with other medications? While generally safe, it’s essential to discuss all medications with your doctor, as spacing it from certain medications (like thyroid hormones) may be recommended.
- Does it increase iron levels in the blood? Minimal systemic iron absorption significantly reduces the risk of iron overload.
- Is it suitable for non-dialysis CKD patients? While primarily prescribed for dialysis phosphate management, a doctor may recommend it for non-dialysis patients in certain circumstances.
- What are the common side effects? Mild gastrointestinal issues like diarrhea or dark stools are the most common side effects of sucroferric oxyhydroxide in CKD, and these are usually well-tolerated.
Why Sucroferric Oxyhydroxide Is the Future of Hyperphosphatemia Treatment?
Sucroferric oxyhydroxide offers several key advantages:
- Proven Clinical Success: Extensive global studies support its efficacy in managing hyperphosphatemia.
- Reduced Patient Burden: Fewer tablets translate to better compliance and improved quality of life.
- Favorable Safety Profile: Lower risk of vascular calcification and systemic toxicity compared to traditional binders.
- Sustainability: Unlike aluminum-based binders, it poses no long-term toxicity risks.
WBCIL’s Commitment to High-Quality Iron-Based APIs
West Bengal Chemical Industries Limited (WBCIL) is a trusted leader in the development and manufacturing of high-quality, GMP-certified pharmaceutical ingredients, specializing in iron-based APIs. Our portfolio includes:
- Sucroferric Oxyhydroxide: Sucroferric oxyhydroxide chemical compound, a superior phosphate binder for CKD patients.
- Ferric Carboxymaltose: Ferric carboxymaltose chemical compound, an injectable iron therapy for anemia.
- Iron Polymaltose Complex: Iron polymaltose complex, an effective oral iron supplement.
- Ferric Citrate: Ferric citrate chemical compound, a dual-action phosphate binder for CKD and iron supplement.
- Ferric Maltol: Ferric maltol chemical compound, an oral iron supplement.
WBCIL is committed to:
- GMP-certified production processes.
- Continuous research and development.
- Adherence to global regulatory standards, including USP, BP, and EP.
Conclusion
Sucroferric oxyhydroxide is transforming the landscape of hyperphosphatemia management. Its high phosphate-binding efficiency, low pill burden, and excellent safety profile offer a significant advantage for CKD patients on dialysis. If you are struggling with hyperphosphatemia, discuss sucroferric oxyhydroxide with your healthcare provider to see if it’s the right treatment option for you.
