Liposomal Technology
What are liposomes?
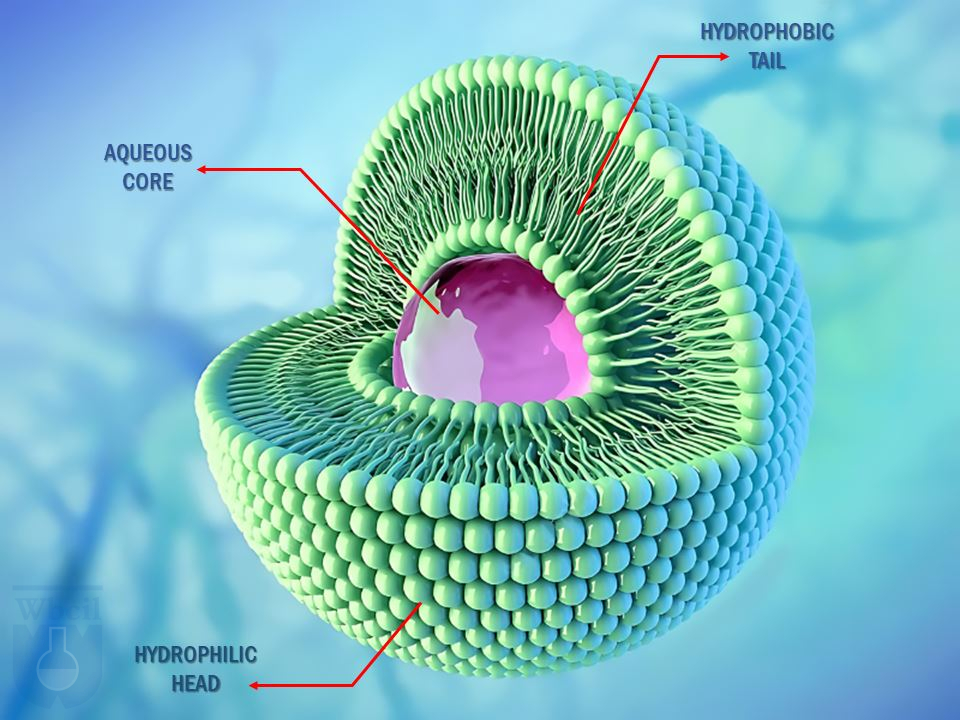
- Tiny, spherical vesicles made of phospholipids.
- Encapsulates active ingredients.
- Improves absorption and bioavailability.
- Protects ingredients from degradation.
- Can target specific cells or tissues.
- Used in medicine, nutrition, cosmetics, and vaccines.
- Challenges include complex production and stability issues.
Leading manufacturer of high-quality APIs since 1962. Committed to excellence, we deliver superior APIs meeting stringent WHO-GMP, GMP, ISO, IEC, HACCP, QMC, and FSSAI standards. Our expertise extends to innovative liposomal formulations, ensuring the same exceptional quality and reliability. Trust us for your API needs.
Our Liposomal Product Offerings
- Superior Encapsulation: Maximum active ingredient delivery to target sites.
- Enhanced Bioavailability: Protected from stomach acids for optimal absorption.
- Diverse Product Forms: tablets, granules, pellets, suspension and powders to suit your needs.
- Customized Coatings: We offer a range of coating options to further enhance the performance and stability of your liposomal products. These coatings can help to:
– Protect active ingredients from degradation.
– Improve solubility and bioavailability.
– Control the rate of release.
– Target specific tissues or organs.
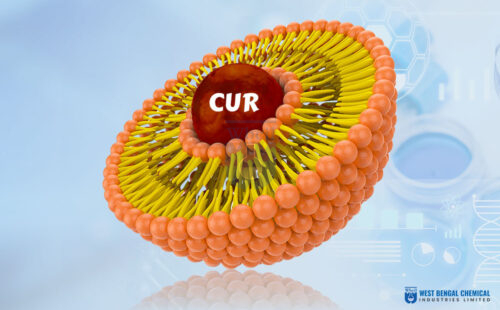
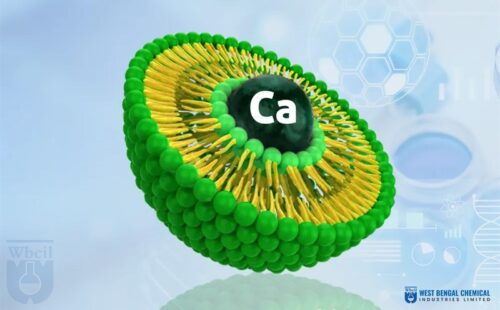
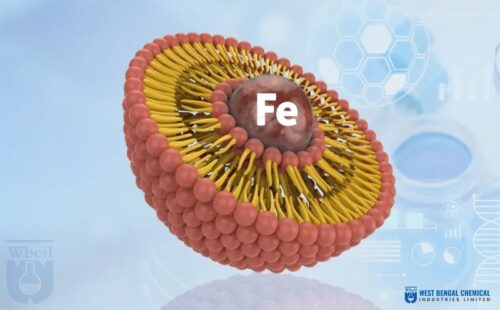
Liposomal technology is a cutting-edge delivery system that uses tiny spherical vesicles, called liposomes, made of phospholipid bilayers. These vesicles encapsulate nutrients or drugs, allowing them to be delivered directly to cells for maximum absorption and bioavailability.
Liposomes mimic the body’s natural cell membranes, enabling them to bypass digestive enzymes and deliver active ingredients directly to target cells. This ensures that the nutrients or drugs remain stable and effective until they reach their destination.
- Enhanced bioavailability and absorption.
- Reduced side effects (e.g., gastrointestinal discomfort).
- Targeted delivery of active ingredients to cells.
- Improved stability of sensitive compounds like vitamins or APIs.
- Longer shelf life due to protection from degradation.
Traditional delivery systems, like tablets or powders, often lose effectiveness during digestion. Liposomal technology, on the other hand, protects the active ingredient from degradation in the stomach, ensuring better absorption and minimal waste.
Liposomal technology minimizes resource consumption, generates less waste, and requires fewer synthetic stabilizers compared to alternatives like polymeric nanoparticles or nanoemulsions. It’s a sustainable choice for pharmaceutical and nutraceutical applications.
Liposomal technology is widely used in:
- Pharmaceutical APIs (e.g., liposomal iron for anemia, liposomal magnesium for stress).
- Nutraceuticals (e.g., liposomal Vitamin C for immunity).
- Cosmetics (e.g., anti-aging creams and serums).
- Oncology treatments (e.g., targeted cancer therapies).
- Micelles rely on surfactants and are less stable than liposomes.
- Nanoemulsions can struggle with absorption and require synthetic additives.
- Liposomal technology offers superior absorption, better stability, and eco-friendly production practices, making it the preferred choice for high-quality products.
Yes, liposomal APIs are safe when manufactured under strict quality standards, like WBCIL’s GMP-certified processes. They minimize side effects and ensure consistent performance.
WBCIL specializes in:
- Liposomal Iron for treating anemia.
- Liposomal Calcium for bone health.
- Liposomal Magnesium for stress relief and muscle recovery.
- Liposomal Zinc for immune health and skin repair.
The phospholipid bilayer of liposomes protects active ingredients from stomach acid and enzymes, ensuring they reach the bloodstream intact. This improves bioavailability significantly compared to traditional delivery methods.
Liposomal technology has transformative applications in:
- Pharmaceuticals: Targeted drug delivery and APIs.
- Nutraceuticals: Enhancing the efficacy of dietary supplements.
- Cosmetics: Delivering active ingredients to deeper skin layers.
- Oncology: Reducing toxicity in cancer treatments.
Liposomal delivery systems generally have minimal side effects because they reduce direct interaction with the stomach lining. For example, WBCIL’s liposomal iron minimizes gastrointestinal discomfort compared to traditional iron supplements.
WBCIL offers:
- GMP-certified manufacturing for consistent quality.
- High-purity liposomal APIs.
- A wide portfolio of innovative liposomal solutions tailored for diverse applications.
WBCIL follows Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and adheres to stringent international quality standards to produce APIs with maximum potency, stability, and safety.
Yes, WBCIL provides customizable liposomal APIs that can be integrated into pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, or cosmetics, meeting specific market and client needs.
While liposomal products may initially seem more expensive, their superior efficacy and reduced dosages make them cost-effective in the long run.
Simply contact the WBCIL team via mailing us at [email protected] to discuss your requirements. We’ll guide you through the process of integrating our liposomal APIs into your formulations.
With growing demand for sustainable and efficient delivery systems, liposomal technology is poised to dominate pharmaceuticals, nutraceuticals, and cosmetics for years to come.
Liposomes can be classified based on their size, number of bilayers, and surface charge. Common types include small unilamellar vesicles (SUVs), large unilamellar vesicles (LUVs), giant unilamellar vesicles (GUVs), and multilamellar vesicles (MLVs).
Liposome stability is influenced by factors such as temperature, pH, ionic strength, and the presence of surfactants or other additives.
Phospholipids are amphiphilic molecules that spontaneously self-assemble into bilayers in aqueous environments, forming the basic structure of liposomes.
High absolute values of zeta potential (typically > |30| mV) indicate good colloidal stability, preventing liposome aggregation.
Common phospholipids include phosphatidylcholine (PC), phosphatidylethanolamine (PE), phosphatidylserine (PS), and phosphatidylinositol (PI).