-
Product Name:
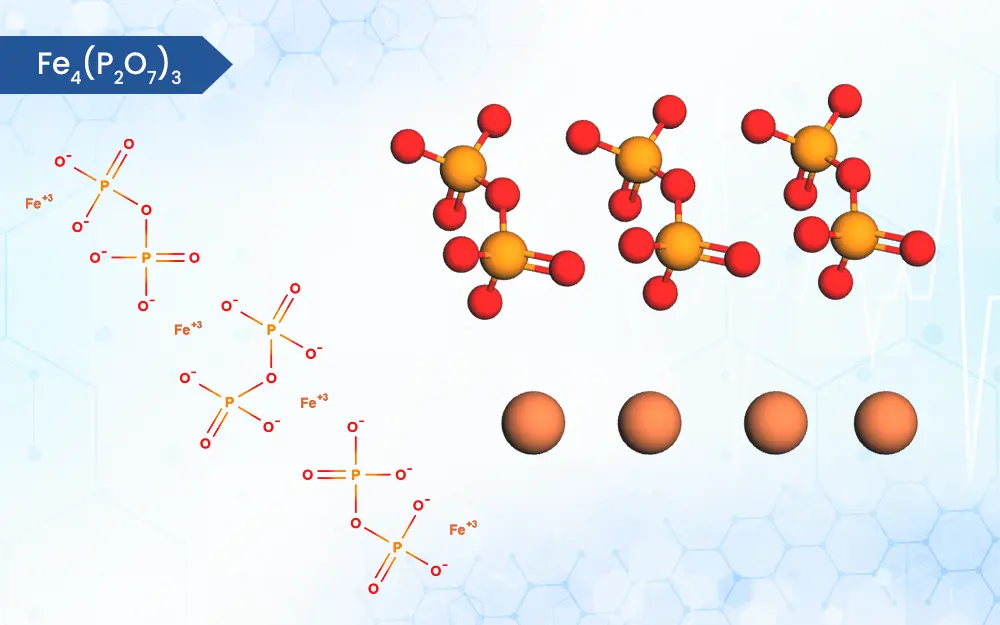
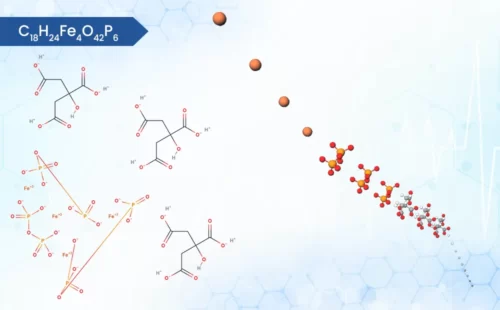
Ferric Pyrophosphate
-
Molecular Formula:
Fe4(P2O7)3
-
Molecular Weight:
745.21 g/mol
-
CAS No.:
10058-44-3
-
HSN Code:
2835
-
CID Code:
24877
-
Shelf Life:
3 years - 20°C powder
-
DrugBank ID
DB09147
-
ChemSpider ID
23258
-
UNII No.
QK8899250F
- USP
- IUPAC Names
- Synonyms
- MSDS
USP of Ferric Pyrophosphate
- Fights iron deficiency anemia.
- Gentler on the stomach than other iron supplements.
- Its almost white colour is exclusively used for iron fortification in food with light colour, like rice, wheat etc.
- Flame retardant in textiles.
- Ingredient in pigments like Prussian Blue.
- Speeds up plastic and resin production.
- Helps create eco-friendly hydrogen peroxide.
IUPAC Names of Ferric Pyrophosphate
iron(3+);phosphonato phosphate
Synonyms of Ferric Pyrophosphate
- ferric pyrophosphate
- ferric pyrophosphate nonahydrate
- Iron(III) pyrophosphate
- CAS No. 10058-44-3
- Iron pyrophosphate
- Iron(3+) pyrophosphate
- Diphosphoric acid, iron(3+) salt (3:4)
- Tetrairon tris(pyrophosphate)
- Diphosphoric acid, iron(3++) salt
- iron(3+);phosphonato phosphate
- Iron(III) diphosphate
- Diphosphoric acid, iron(3+) salt
- UNII No. QK8899250F
- Iron(III) pyrophosphate soluble crystals;Iron(III) pyrophosphate soluble crystals
- Pyrophosphoric acid, iron(3+) salt (3:4)
- UNII-QK8899250F
- ferric diphosphate
- iron(3+) diphosphate
- Iron(III)pyrophosphate
- Diphosphoric acid iron(3+) salt (3:4)
- Iron (as pyrophosphate)
- Diphosphoric acid, iron(3+) salt (1:?)
- Iron (III) pyrophosphate
- tetrairon tris(diphosphate)
- iron(3+) diphosphate (4/3)
- Iron (lll) pyrophosphate hydrate
- Iron(III) pyrophosphate tribasic
- Iron(III) diphosphate (Fe4(P2O7)3)
- Iron(III) pyrophosphate, soluble crystals
MSDS of Ferric Pyrophosphate
Download MSDS PDF- INHALATION: Move exposed person to fresh air. If not breathing, seek immediate medical attention. If breathing is irregular or if respiratory arrest occurs, provide artificial respiration or oxygen by trained personnel and seek medical attention
- INGESTION: Do not induce vomiting unless directed to do so by medical personnel. Never give anything by mouth to an unconscious person. Seek medical attention.
- SKIN CONTACT: Remove contaminated clothing and shoes and immediately flush skin with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes. Wash clothing before reuse. Clean shoes thoroughly before reuse. If irritation persists, seek medical attention.
- EYE CONTACT: Check for and remove any contact lenses. Immediately flush eyes with plenty of water for at least 15 minutes, occasionally lifting the upper and lower eyelids.
- HAZARDOUS COMBUSTION PRODUCTS: Decomposition products may include oxides of carbon and iron.
- FIRE: Not considered a fire hazard.
- EXPLOSION: Not considered an explosion hazard.
- FIRE EXTINGUISHING MEDIA: Use fire-extinguishing media appropriate to the surrounding fire.
- SPECIAL INFORMATION: In the event of a fire, wear full protective clothing and NIOSH approved self-contained breathing apparatus with full-face piece operated in the pressure demand or other positive pressure mode.
- ENGINEERING CONTROLS: Use process enclosures, local exhaust ventilation, or other engineering controls to keep airborne levels below recommended exposure limits. If user operations generate dust, fume or mist, use ventilation to keep exposure to airborne Contaminants below the exposure limit.
- PERSONAL PROTECTION: Safety glasses, Lab Coat, Dust respirator, be sure to use an approved / certified respirator or equivalent, Gloves
- PERSONAL PROTECTION IN CASE OF A LARGE SPILL: Splash goggles. Full suit. Dust respirator. Boots. Gloves. A self-contained breathing apparatus should be used to avoid inhalation of the product. Suggested protective clothing might not be sufficient; consult a specialist BEFORE handling this product.
- EXPOSURE LIMITS: Consult local authorities for acceptable exposure limits.
- Appearance Form: Powder
- Color: White or yellow white
- Odour: Characteristic
- Solubility: Insoluble in water, soluble in mineral acid
Description of Ferric Pyrophosphate
Ferric pyrophosphate, a key iron source in some dietary supplements, boasts distinct physical and chemical properties. It exists as a yellowish-white to beige crystalline solid [1]. Unlike many iron compounds, it’s practically insoluble in water, rendering it odorless and tasteless [1]. Its white colour is special and a very crucial reason for its use in iron fortification. Ferric pyrophosphate also exhibits low hygroscopicity, meaning it doesn’t readily absorb moisture from the air, contributing to its stability as a supplement [2].
On the scientific side, this compound is an iron coordination entity, formed by the linkage of ferric (Fe3+) cations and diphosphate (P2O74-) anions in a 4:3 ratio [1]. This specific structure plays a crucial role in its function, as it ensures the iron is securely bound, potentially reducing unwanted side effects observed with free iron intake. As a leading API manufacturer, WBCIL Ferric pyrophosphate prioritizes strict CGMP and ISO quality control measures throughout the production process. The prolonged experience from 1962 ensures consistent potency, purity, and safety in every dose of WBCIL’s ferric pyrophosphate.
Application of Ferric Pyrophosphate
Food and Beverage Industry
- Cereals and Flours: Added to cereals, flours, and baked goods to enhance their iron content and address dietary deficiencies.
- Beverages: Used in drinks, including juices and dairy products, to provide an additional source of iron.
- Infant Formula: Included in infant formulas to ensure adequate iron intake for proper growth and development.
Pharmaceutical Industry
Oral Supplements
- Iron Tablets and Capsules: Formulated in oral iron supplements to treat or prevent iron deficiency anemia.
- Iron-Enhanced Gummies and Chewable: Used in child-friendly iron supplements that are easy to consume.
Dialysis Solutions
Hemodialysis: Added to dialysis solutions (Ferric Pyrophosphate Citrate) for patients with chronic kidney disease to maintain adequate iron levels and reduce anemia.
Medical Nutrition
Enteral Nutrition
Medical Foods: Incorporated into enteral nutrition formulas for patients who require tube feeding, ensuring they receive essential nutrients, including iron.
Specialized Diets
Therapeutic Diets: Used in therapeutic diets for individuals with specific medical conditions that cause iron deficiency.
Agriculture Industry
Animal Feed
- Livestock and Poultry Feed: Added to animal feed to prevent iron deficiency and promote healthy growth and development in livestock and poultry.
- Pet Food: Included in pet food formulations to ensure pets receive adequate iron in their diet.
Biotechnology and Research
Nutritional Studies
Iron Bioavailability Research: Used in studies to evaluate the bioavailability and efficacy of iron in various formulations and delivery systems.